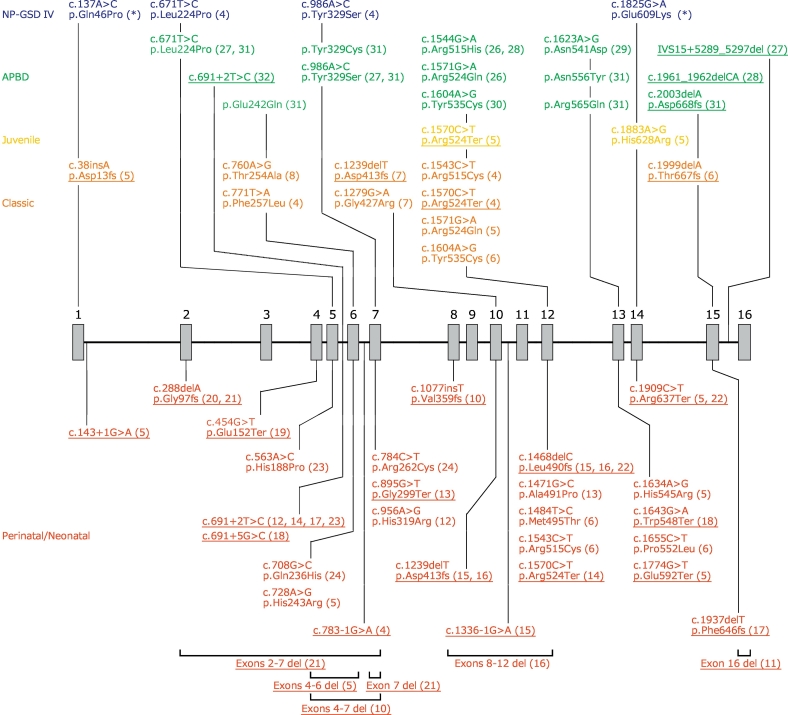
Fig. 1.
Organization of the GBE1 gene, and disease-associated mutations hitherto reported.
The number above each box indicates the exon number. References are denoted in parentheses. The mutations identified in our patient are indicated by an asterisk. Null mutations such as intragenic deleterious, nonsense, frameshift, and splice-site mutations are underlined. Herein, we gathered neonatal and perinatal forms in a mass because their diagnostic criteria are not strictly determined and clinical outcomes in these forms do not differ significantly. Null mutations, except for those located in exons 15 and 16, tend to associate with more severe forms of glycogen storage disease type IV (GSD IV), such as classic hepatic form or perinatal/neonatal neuromuscular forms. The same mutations are often reported in unrelated patients with milder forms, such as non-progressive-GSD IV (NP-GSD IV) and adult polyglucosan body disease (APBD).