Abstract
Strigolactones (SLs) regulate diverse developmental phenomena. Rice SL biosynthesis and signaling mutants have an increased number of tillers and a reduced plant height relative to wild-type (WT) rice plants. In this study, we tested the effectiveness of gibberellin (GA) on restoring more tillering phenotype and dwarfism observed in both SL biosynthesis and signaling mutants. The application of GA to these mutants rescued the tiller bud outgrowth; however, the sensitivity to GA was different between the WT and the SL biosynthesis mutant.
Keywords: strigolactone, gibberellin, tiller bud outgrowth, hormone cross-talk
Introduction
Shoot branching, an important agronomic trait that determines crop yield, is primarily controlled by plant hormones. Auxin and cytokinin are major hormones that control shoot branching. Strigolactone (SL), a member of a new class of phytohormones, is also known to control shoot branching.1,2) The relationship between the two classical hormones (auxin and cytokinin) and SLs in the regulation of shoot branching has been actively discussed with regard to rice, Arabidopsis, and pea plants.3–5)
SLs are branching inhibitors biosynthesized from beta-carotene by beta-carotene isomerase (D27), two carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases (D10 and D17), and P450s (Os01g0700900 and Os01g0701400) in rice.6,7) The SL signaling component D3 encodes an F-box leucine-rich repeat (LRR)-containing protein, which functions downstream of this branching inhibitor.8) After the discovery of SL as a branching inhibitor, a rice mutant, d14/d88/htd2, which encodes the SL receptor, has been reported to be defective in novel genes that transduce the SL signal.9–11) The d14 and d3 mutants are insensitive to exogenous SL application and contain higher levels of SL than wild-type (WT) plants.9–11) Rice mutants defective in both SL biosynthesis and signal transduction also exhibit partial dwarfism.12)
Gibberellin (GA) is a crucial plant hormone that regulates developmental processes throughout the life cycle of plants.13) Plants defective in both GA biosynthesis and GA signal transduction show typical phenotypes such as dwarfism; small, dark green leaves; prolonged germination dormancy; retardation of root growth; suppression of flowering; reduced seed production; and male sterility.13) Although it is reported that GA-deficient rice plants also exhibit early and increased tillering and dwarfism,14,15) there have been no reports of the relationship between GA signaling and SL signaling in the tillering and dwarfism of rice plants. This report investigated the relationship between GA and SL in controlling tiller bud outgrowth and plant height.
Materials and Methods
1. Plant materials
The wild-type rice varieties (Oryza sativa) used in this study were Shiokari (d3-1, d10-1, d14-1, d17-1, and d27-1)9,12,16) and Nipponbare (d10-2).17)
2. Rice hydroponic culture
Rice seeds were sterilized in 2.5% sodium hypochlorite solution containing 0.01% Tween 20 for 30 min, washed with sterile water six times, and incubated in sterile water at 25°C in the dark for 2 days. Germinated seeds were transferred into hydroponic culture media2) solidified with 0.6% agar and cultured at 25°C under fluorescent white light with a 14-hr light and 10-hr dark photoperiod for 6 days. Each seedling was transferred to a brown glass vial containing 12 mL of hydroponic culture solution with or without GA3 or GR24 (synthetic SL analog)18) and grown under the same condition for 7 days. Plant height was measured from the ground to the tip of the longest leaf of the plant.
For prolonged cultivation, 2-week-old rice seedlings were transferred to a new vial containing 12 mL of hydroponic culture solution with or without GA3 and grown under the same condition for 7 days.
Results and Discussion
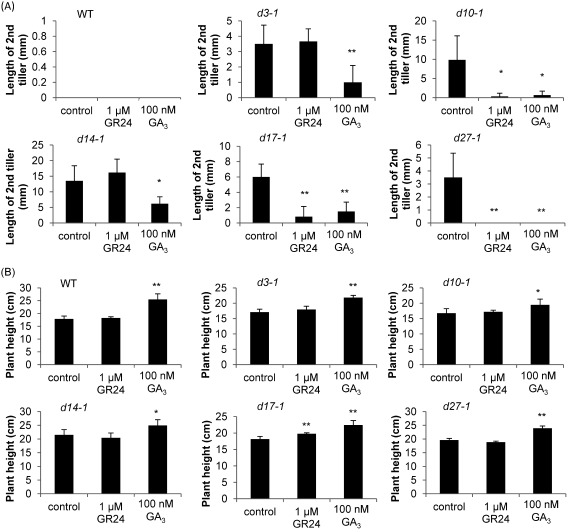
The growth of second tiller buds in SL mutants, such as d3-1, d10-1, d14-1, d17-1, and d27-1, was observed when 2-week-old rice seedlings were grown hydroponically, but those of WT plants remained dormant.2) To assess the role of GA in SL mutants, we first examined the effect of GA3 on the outgrowth of second tiller buds and the plant height of mutants defective in SL biosynthesis (d10-1, d17-1, and d27-1) and signaling (d3-1 and d14-1). Two-week-old WT rice ‘Shiokari’ did not show elongation of the second tiller as previously reported.2) On the other hand, following application of GA3 but not SL, the outgrowth of second tiller buds in all of the mutants was significantly suppressed, and plant height in these mutants increased. The application of GR24 suppressed tiller bud outgrowth in SL biosynthesis mutants (d10-1, d17-1, and d27-1) but not in SL signaling mutants (d3-1 and d14-1). In addition, GR24 treatment did not produce any increase in the plant height of these mutants (Fig. 1A and B).
Fig. 1. Effects of SL and GA on tiller bud outgrowth and plant height in 2-week-old rice seedlings. (A) Lengths of second tillers in 2-week-old seedlings. The data are means±SD of six samples. (B) Plant heights of 2-week-old seedlings. The data are means±SD of six samples. * (p<0.05) and ** (p<0.01) indicate significant differences relative to controls.
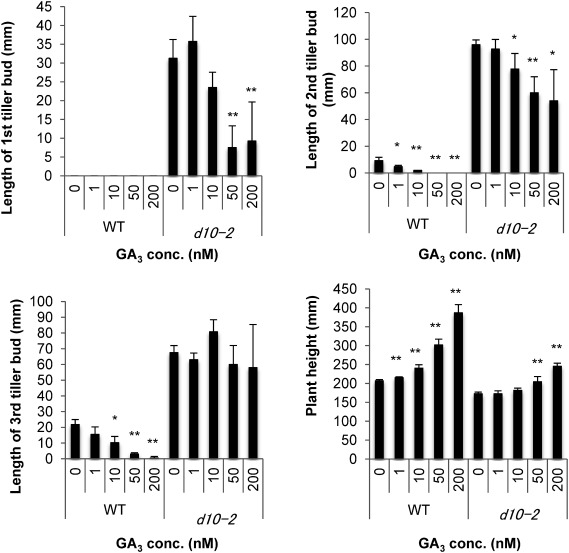
Next, we estimated the differences in GA sensitivity between WT ‘Nipponbare’ and d10-2 rice seedlings. Two-week-old rice seedlings did not show second and third tiller bud outgrowth in the WT, but the second and third tiller buds grew out in hydroponically grown 3-week-old rice seedlings of both the WT and d10-2 mutants.2) The effects of GA3 were determined by measuring the tiller lengths and plant heights in 3-week-old seedlings. In the WT, GA3 treatment suppressed the elongation of the second and third tiller buds and increased plant height in a concentration-dependent manner. In the d10-2 mutant, although the elongation of the first and second tiller buds and the increase in plant height showed tendencies similar to those in the WT treated with GA3, its responses to GA3 were weaker than those of the WT (Fig. 2). The outgrowth of the second tiller buds was significantly inhibited in the d10-2 mutant by treatment with 10 nM and 50 nM GA3, whereas it was significantly suppressed in WT plants with only 1 nM GA3 (Fig. 2). Plant height was also significantly increased in the d10-2 mutant by treatment with 50 nM and 200 nM GA3, whereas it was significantly elongated in WT plants with 1 nM GA3 (Fig. 2). In addition, the outgrowth of the third tiller bud was not suppressed by the GA3 treatment. These results indicate the existence of novel cross-talk between SL and GA signaling in the outgrowth of tiller buds and elongation of plant height.
Fig. 2. Effect of GA on tiller bud growth and plant height in 3-week-old rice. First, second, and third tiller bud lengths and plant heights of 3-week-old rice. Using a t-test, the significant difference of * (p<0.05) and ** (p<0.01) as compared to 0 nM GA3-treated plants was obtained. Data are means±SD (n=6).
GA and SL can reduce the number of tillers or branching. In Arabidopsis, it has been reported that both SL and GA regulate auxin transport.19,20) It is suspected that both SL and GA may play a role in regulating tiller bud outgrowth by regulating auxin transport. In addition, Luisi et al. (2011) reported that the endogenous level of bioactive GA modulates the response of decapitated pea plants to SL, suggesting the possible involvement of the auxin transport in SL–GA cross-talk.21) However, the ways SL and GA regulate auxin transport appear to be different: SL promotes the accumulation of PIN proteins, whereas GA represses the accumulation of PIN proteins.19,20) This may be one of the reasons GA sensitivity in tiller bud outgrowth and the increase in plant height were different between the WT and the d10-2 mutant.
SL regulates various morphological changes, such as branching, leaf senescence, root hair elongation, and mesocotyl elongation.1,2,22–25) Because auxin, cytokinin, and gibberellin also control similar morphological changes with SL, studies of SL-signaling cross-talk with auxin and cytokinin continue to expand. However, there are very few reports on the cross-talk between SL and GA. Notably, de Saint Germain et al. (2013) reported that SL acts independently of GA in stimulating internode elongation in pea plants.26) Recently, we found two evidences of the existence of cross-talk between SL and GA signaling. One is the SL-dependent interactions of D14 with SLR1, which is one of the components of GA signaling in vitro and in vivo.27) Another is the GA-signaling-dependent regulation of the expression levels of SL biosynthesis genes.28) In the present study, we found that the responses to GA in tiller bud outgrowth and plant elongation were different in the WT and d10-2 mutants. Our findings indicate the existence of physiological cross-talk between SL and GA in not only the regulation of SL biosynthesis but also tiller bud outgrowth and plant elongation. Further investigation will reveal the important mechanism of SL–GA cross-talk that is useful for controlling the morphological changes affecting crop yield.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST).
References
- 1).V. Gomez-Roldan, S. Fermas, P. B. Brewer, V. Puech-Pagès, E. A. Dun, J. P. Pillot, F. Letisse, R. Matusova, S. Danoun, J. C. Portais, H. Bouwmeester, G. Bécard, C. A. Beveridge, C. Rameau and S. F. Rochange: Nature 455, 189–194 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2).M. Umehara, A. Hanada, S. Yoshida, K. Akiyama, T. Arite, N. Takeda-Kamiya, H. Magome, Y. Kamiya, K. Shirasu, K. Yoneyama, J. Kyozuka and S. Yamaguchi: Nature 455, 195–200 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3).J. Xu, M. Zha, Y. Li, Y. Ding, L. Chen, C. Ding and S. Wang: Plant Cell Rep. 34, 1647–1662 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4).H. Sun, J. Tao, M. Hou, S. Huang, S. Chen, Z. Liang, T. Xie, Y. Wei, X. Xie, K. Yoneyama, G. Xu and Y. Zhang: Ann. Bot. 115, 1155–1162 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5).H. Sun, J. Tao, S. Liu, S. Huang, S. Chen, X. Xie, K. Yoneyama, Y. Zhang and G. Xu: J. Exp. Bot. 65, 6735–6746 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6).A. Alder, M. Jamil, M. Marzorati, M. Bruno, M. Vermathen, P. Bigler, S. Ghisla, H. Bouwmeester, P. Beyer and S. Al-Babili: Science 335, 1348–1351 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7).Y. Zhang, A. D. van Dijk, A. Scaffidi, G. R. Flematti, M. Hofmann, T. Charnikhova, F. Verstappen, J. Hepworth, S. van der Krol, O. Leyser, S. M. Smith, B. Zwanenburg, S. Al-Babili, C. Ruyter-Spira and H. J. Bouwmeester: Nat. Chem. Biol. 10, 1028–1033 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8).P. Stirnberg, K. van De Sande and H. M. Leyser: Development 129, 1131–1141 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9).T. Arite, M. Umehara, S. Ishikawa, A. Hanada, M. Maekawa, S. Yamaguchi and J. Kyozuka: Plant Cell Physiol. 50, 1416–1424 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10).Z. Gao, Q. Qian, X. Liu, M. Yan, Q. Feng, G. Dong, J. Liu and B. Han: Plant Mol. Biol. 71, 265–276 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11).W. Liu, C. Wu, Y. Fu, G. Hu, H. Si, L. Zhu, W. Luan, Z. He and Z. Sun: Planta 230, 649–658 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12).S. Ishikawa, M. Maekawa, T. Arite, K. Onishi, I. Takamure and J. Kyozuka: Plant Cell Physiol. 46, 79–86 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13).S. Yamaguchi: Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59, 225–251 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14).S. F. Lo, S. Y. Yang, K. T. Chen, Y. I. Hsing, J. A. Zeevaart, L. J. Chen and S. M. Yu: Plant Cell 20, 2603–2618 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15).S. Ito, N. Kitahata, M. Umehara, A. Hanada, A. Kato, K. Ueno, K. Mashiguchi, J. Kyozuka, K. Yoneyama, S. Yamaguchi and T. Asami: Plant Cell Physiol. 51, 1143–1150 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16).H. Lin, R. Wang, Q. Qian, M. Yan, X. Meng, Z. Fu, C. Yan, B. Jiang, Z. Su, J. Li and Y. Wang: Plant Cell 21, 1512–1525 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17).T. Arite, H. Iwata, K. Ohshima, M. Maekawa, M. Nakajima, M. Kojima, H. Sakakibara and J. Kyozuka: Plant J. 51, 1019–1029 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18).E. M. Mangnus and B. Zwanenburg: J. Agric. Food Chem. 40, 1066–1070 (1992). [Google Scholar]
- 19).S. Crawford, N. Shinohara, T. Sieberer, L. Williamson, G. George, J. Hepworth, D. Müller, M. A. Domagalska and O. Leyser: Development 137, 2905–2913 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20).B. C. Willige, E. Isono, R. Richter, M. Zourelidou and C. Schwechheimer: Plant Cell 23, 2184–2195 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21).A. Luisi, R. Lorenzi and C. Sorce: Plant Growth Regul. 65, 415–419 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 22).Y. Yamada, S. Furusawa, S. Nagasaka, K. Shimomura, S. Yamaguchi and M. Umehara: Planta 240, 399–408 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23).H. Koltai: New Phytol. 190, 545–549 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24).S. Ito, T. Nozoye, E. Sasaki, M. Imai, Y. Shiwa, M. Shibata-Hatta, T. Ishige, K. Fukui, K. Ito, H. Nakanishi, N. K. Nishizawa, S. Yajima and T. Asami: PLoS ONE 10, e0119724 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25).Z. Hu, H. Yan, J. Yang, S. Yamaguchi, M. Maekawa, I. Takamure, N. Tsutsumi, J. Kyozuka and M. Nakazono: Plant Cell Physiol. 51, 1136–1142 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26).A. de Saint Germain, Y. Ligerot, E. A. Dun, J. P. Pillot, J. J. Ross, C. A. Beveridge and C. Rameau: Plant Physiol. 163, 1012–1025 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27).H. Nakamura, Y. L. Xue, T. Miyakawa, F. Hou, H. M. Qin, K. Fukui, X. Shi, E. Ito, S. Ito, S. H. Park, Y. Miyauchi, A. Asano, N. Totsuka, T. Ueda, M. Tanokura and T. Asami: Nat. Commun. 4, 2613 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28).S. Ito, D. Yamagami, M. Umehara, A. Hanada, S. Yoshida, Y. Sasaki, S. Yajima, J. Kyozuka, M. Ueguchi-Tanaka, M. Matsuoka, K. Shirasu, S. Yamaguchi and T. Asami: Plant Physiol. 174, 1250–1259 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]