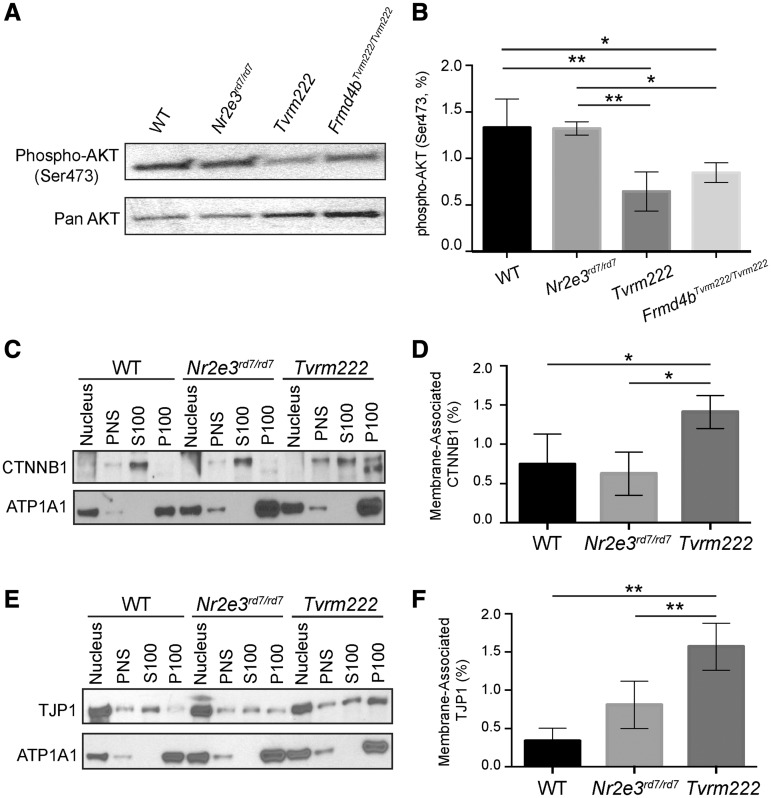
Figure 8.
Phosphorylation of AKT is reduced and membrane-associated CTNNB1 and TJP1 are increased in Tvrm222 mouse retinas. (A, B) Post-nuclear protein extracts from mouse eyecups were analyzed by western blot, probed with the antibody against phosphorylated AKT (Ser473). Pan-AKT was used as the loading control. The western blotting results were quantitated as mean±SD, n = 5 for WT, Nr2e3rd7/rd7 and Tvrm222, n = 4 for Frmd4bTvrm222/Tvrm222; **P = 0.0004, *P = 0.0142 (one-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey’s test). (C–F) Membrane fractionation of mouse eyecups with subsequent western blot analyses of each fraction probed with antibodies against CTNNB1 (C) and TJP1 (E). ATP1A1 was used as the loading control for membrane fractions. Note there is a statistically significant increase in membrane-associated (P100) CTNNB1 and TJP1 in Tvrm222 mouse retinas relative to those in either WT or Nr2e3rd7/rd7 mice. Membrane-associated CTNNB1 and TJP1 were quantified by ImageJ (D, F). The levels of membrane-associated CTNNB1 and TJP1 were normalized to corresponding ATP1A1 levels. Results from four independent experiments were used in the quantification. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. The results are mean±SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. PNS, post-nuclear supernatant; S100, supernatant after 100 000×g centrifugation; P100, pellet after 100 000×g centrifugation.