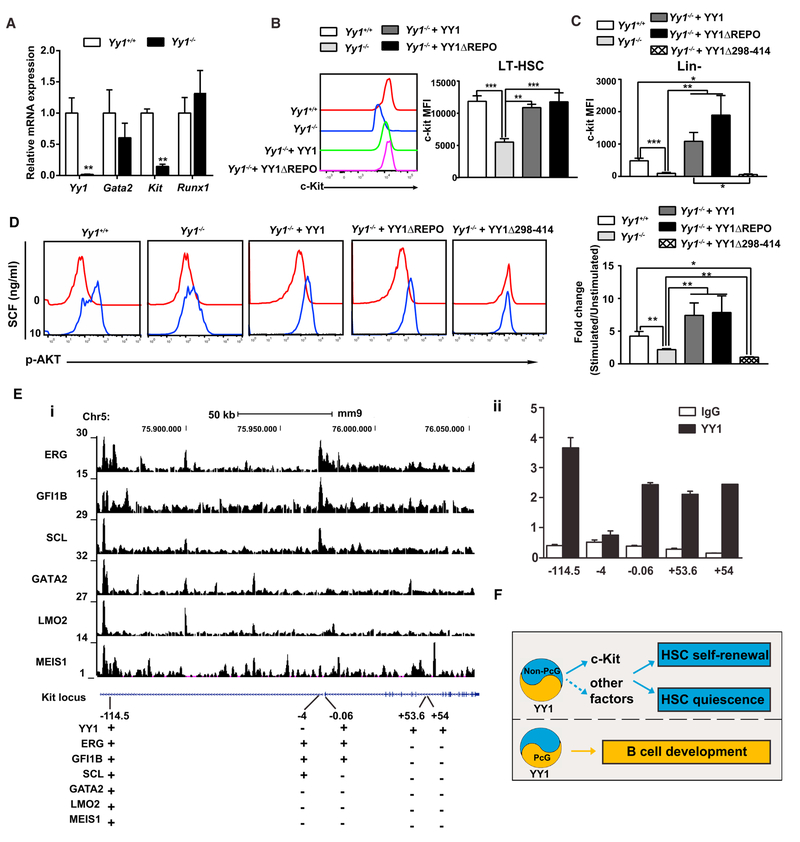
Figure 7. YY1 Promotes SCF/c-Kit Signaling.
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of Yy1, Gata2, Kit, and Runx1 transcript levels in total bone marrow cells.
(B) Evaluation of c-Kit MFI in LT-HSC.
(C) Evaluation of c-Kit MFI in Lin−bone marrow cells.
(D) Phosphorylated flow analysis of AKT.
(E) YY1 occupancy at Kit. (i) “+” and “− ” indicate positive versus negative occupancy of transcription factors at Kit based on ChIP-seq (GEO: GSE22178) or ChIP-qPCR, respectively. (ii) YY1 occupancy at Kit in HPC-7 cells detected by ChIP-qPCR and normalized to input.
(F) The model assumes that YY1 directly regulates SCF/c-Kit signaling in HSCs and promotes HSC long-term self-renewal and quiescence without a requirement for the REPO domain/PcG function. By contrast, YY1 REPO domain/ PcG function is required for Ig rearrangement in early B cells. N represents the number of mice; graphs show means ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.