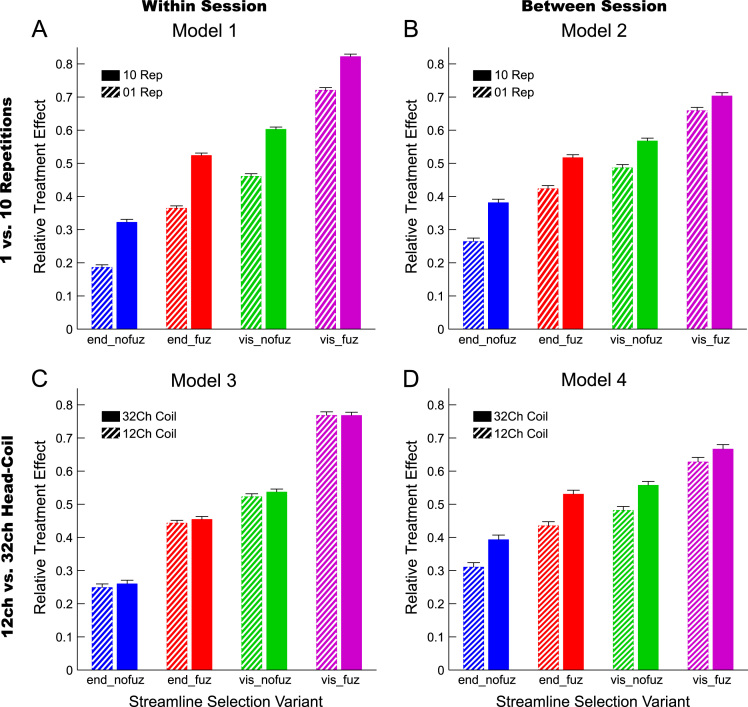
Fig. 2.
Relative treatment effects (RTEs) for the four statistical models. The RTE for a factor combination denotes the probability that a randomly chosen observation for that factor combination yields a higher ICC(2,1) value than a randomly chosen observation from the whole data set. Thus, higher RTEs indicate higher ICC(2,1) values for that factor combination, expressed as a probability value ranging from 0 to 1. Panels depict RTEs for (A) Model 1, within-session reproducibility of reconstruction repetitions×streamline selection variant; (B) Model 2, between-session reproducibility of reconstruction repetitions×streamline selection variant; (C) Model 3, within-session reproducibility of type of head-coil ×streamline selection variant; and (D) Model 4, between-session reproducibility of type of head-coil ×streamline selection variant. Error bars denote the 95% confidence interval of RTEs. End_nofuz, endpoint_nofuzzy; end_fuz, endpoint_fuzzy; vis_nofuz, visiting_nofuzzy; and vis_fuz, visiting_fuzzy streamline selection. 1 Rep, 1 reconstruction repetition; 10 Rep, 10 reconstruction repetitions. 12ch Coil, 12-channel head-coil; 32ch Coil, 32-channel head-coil.