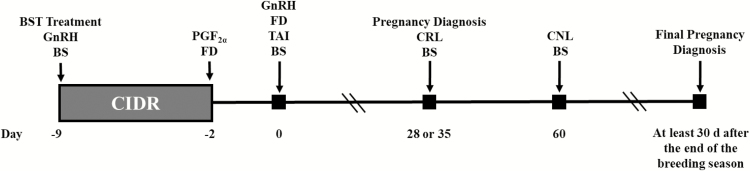
Figure 1.
Schematic of treatments. Heifers assigned to the BST (n = 191) treatment received a 650-mg injection of bovine somatotropin (bST; Posilac; sometribove zinc; Elanco Animal Health, Indianapolis, IN), an injection of GnRH (Factrel; gonadorelin hydrochloride; Zoetis Animal Health, Parssipany, NJ), and a controlled internal drug release (CIDR; EAZI-BREED CIDR; 1.38 g of progesterone; Zoetis Animal Health) insert on day -9; an injection of PGF2α (Lutalyse; dinoprost tromethamine; Zoetis Animal Health) at CIDR removal on day −2; and a second injection of GnRH concurrent with fixed-time AI (TAI) 54 ± 2 h later on day 0. CONTROL heifers (n = 223) were treated the same as BST; however, did not receive an injection of bST on day −9. Blood samples (BS) were collected on day −9, 0, 28, and 60. Follicle diameter (FD) was measured on day −2 and again on day 0. Pregnancy diagnosis was performed by transrectal ultrasonography on day 28 (FL-1, VA-1, and VA-2) or 35 (FL-2) and again at least 30 days after the end of the breeding season. Crown-to-rump length (CRL) was measured on day 28, and crown-to-nose length (CNL) was measured on day 60.