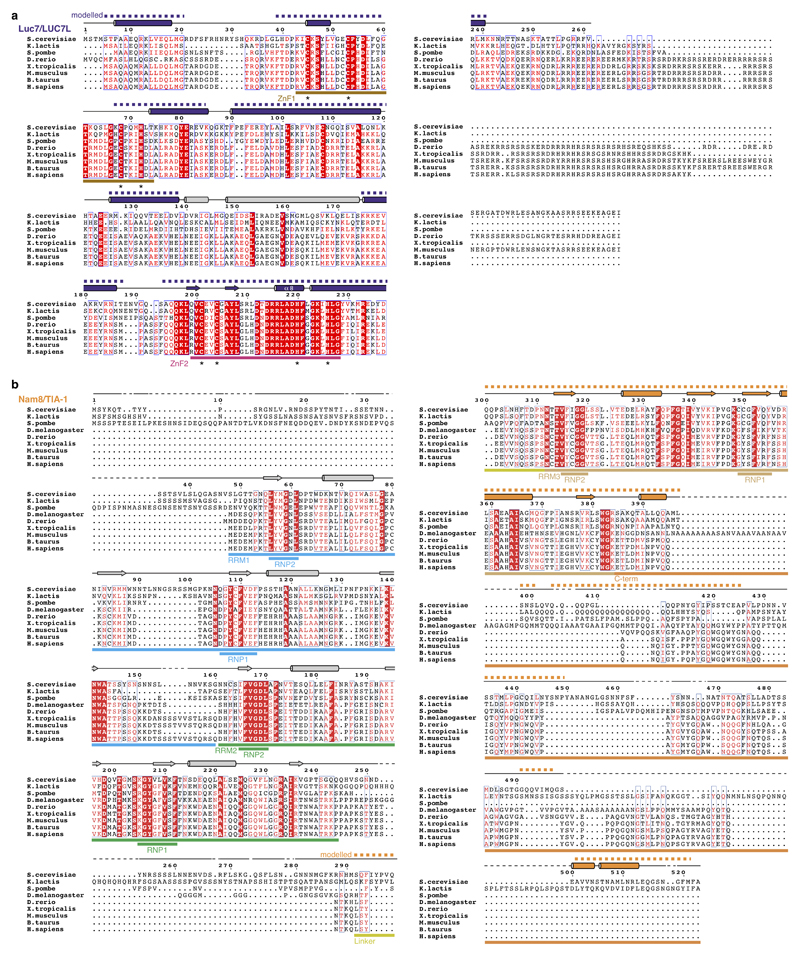
Extended Data Figure 6. Luc7 and Nam8 sequence alignments.
a. The Luc7 (human LUC7-like) amino acid sequence alignment comparing Saccharmoyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces lactis, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Danio rerio, Xenopus tropicalis, Mus musculus, Bos taurus, and Homo sapiens was generated with Clustal Omega and visualized with ESPript 3 (refs 56,57). For the human sequence, LUC7-like 1 was used. Secondary structure elements are indicated above the sequence and derive from the A complex structure (purple) or PSIPRED58 secondary structure prediction (gray). Modelled regions (dashed line) and the Zn-coordinating residues of Zn-finger 1 and 2 (ZnF, asterisk) are indicated. Invariant or conserved residues are highlighted with a red box or red letter font, respectively. b. As panel a but for Nam8 (human TIA-1) comparing Saccharmoyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces lactis, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster, Danio rerio, Xenopus tropicalis, Mus musculus, Bos taurus, and Homo sapiens amino acid sequences. RNA recognition motif, RRM; ribonucleoprotein domain, RNP.