FIGURE 5.
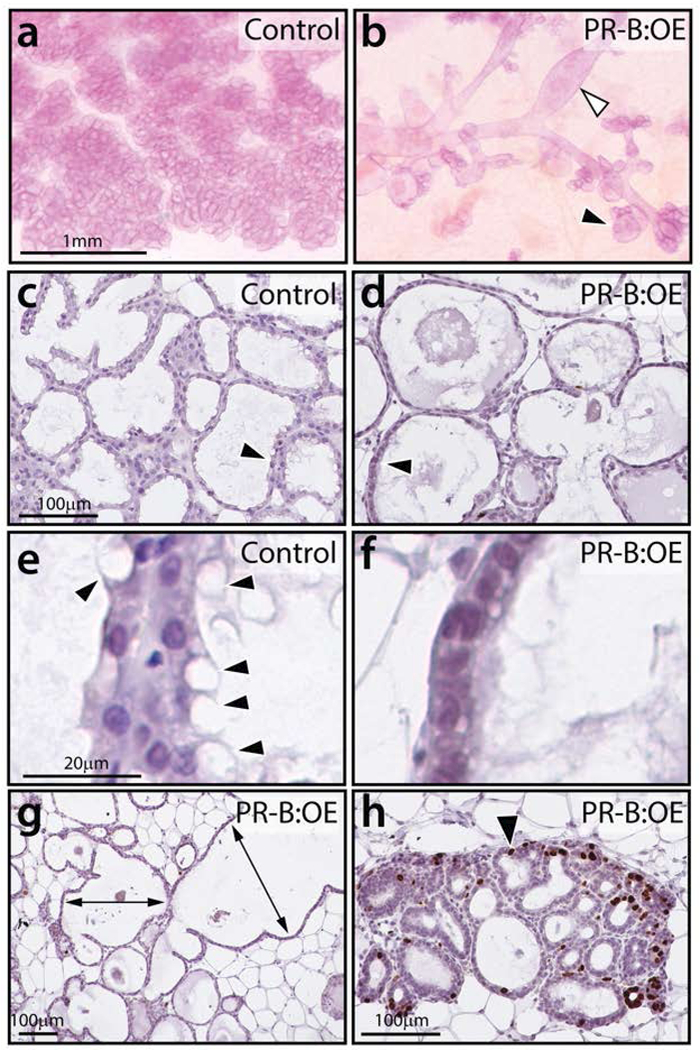
The PR-B:OE mammary gland exhibits an aberrant morphology at lactation. (a) Control mammary gland displays the typical lobuloalveolar structures that completely in-fill the mammary fat pad. (b) The PR-B:OE mammary gland fails to exhibit normal lobuloalveolar morphogenesis. Instead, the PR-B:OE mammary gland shows aberrant dilated ducts (white arrowhead) with abnormal alveolar budding (black arrowhead). (c) Transverse section of lobuloalveolar structures in control mammary gland that are stained for BrdU incorporation. Note the absence of cells scoring positive for BrdU. (d) Transverse section of corresponding PR-B:OE mammary gland, note the overtly distended epithelial ducts (arrowhead). (e) Higher magnification of (c) shows the presence of numerous vacuolated epithelial cells with lipid droplets (arrowheads). (f) Higher magnification of (d) showing the absence of these vacuolated epithelial cells in the PR-OE mammary gland. (g) A low magnification image of the PR-B:OE mammary gland stained for BrdU incorporation. While large areas of the gland do not show regions of proliferation, the PR-B:OE mammary tissue is clearly abnormal with extreme ductal dilation (double headed arrows). (h) shows areas in the PR-B:OE tissue that exhibit foci of epithelial cells with numerous cells scoring positive for BrdU incorporation (black arrowhead). Scale bar in a; c; and e applies to b; d; and f respectively.
