Figure 1.
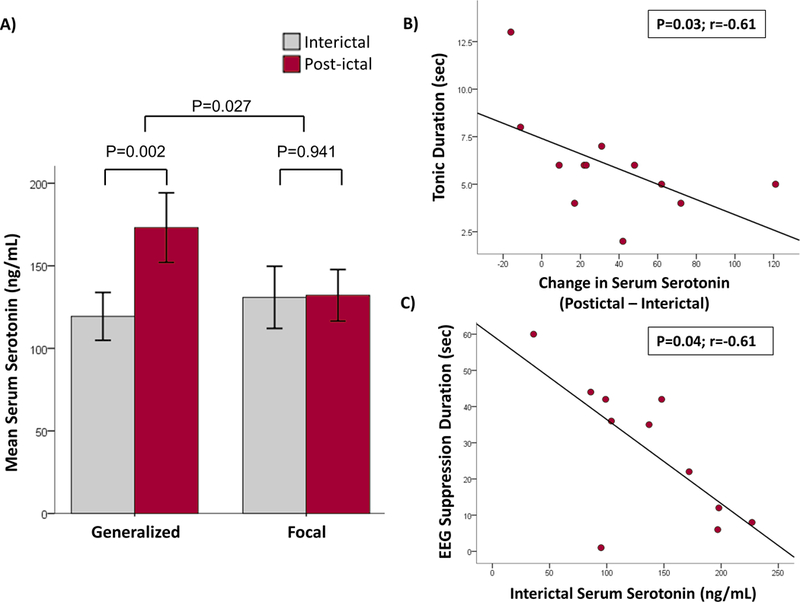
A) Serum serotonin levels increase after seizures. The mean serum post-ictal serotonin levels in ng/mL are shown in red bars and interictal serotonin levels are shown in grey bars for the two seizure groups; Generalized (n=19) and Focal (n=26). Elevated levels of post-ictal serum serotonin after generalized seizures were statistically significant when compared to interictal levels (p=0.002), but not after focal seizures (p=0.941, paired sample T-test). Also, the change in serum serotonin level (post-ictal - interictal) was statistically significant (p=0.027, independent 2 sample T-test) between the generalized and focal seizure groups.
B) Association of tonic duration with serum serotonin. The difference between post-ictal and interictal serum serotonin levels were plotted against the tonic duration of the seizure. Increased levels of serotonin was significantly associated with reduced duration of tonic phase during generalized seizures (n=12).
C) Association of PGES duration with serum serotonin. The interictal serum serotonin levels were plotted against the post-ictal EEG suppression (PGES) duration of the seizure. Higher interictal serotonin was significantly associated with shorter period of EEG suppression during generalized seizures (n=11).
