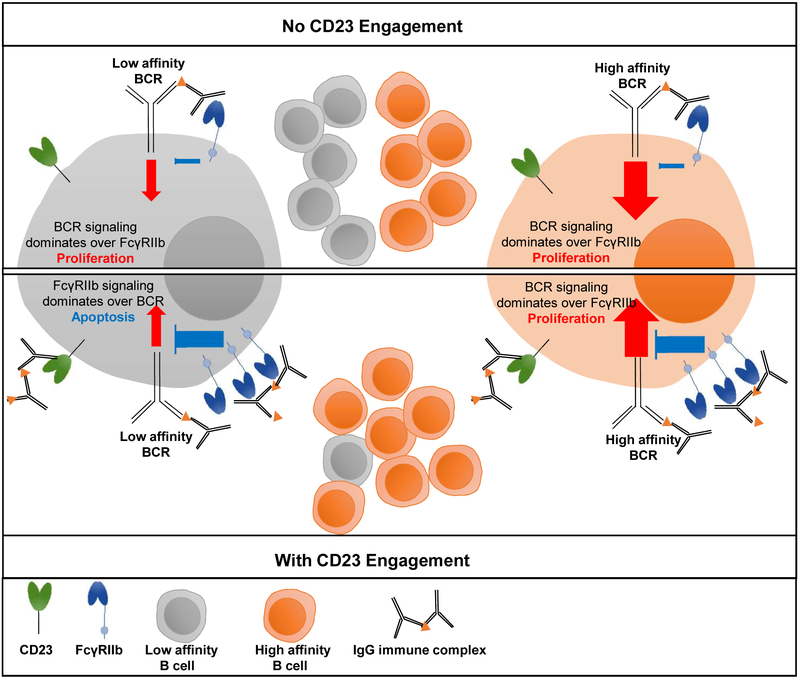
Figure 2: Overview of the coordinated activity of Type I (FcγRIIb) and Type II (CD23) FcγRs in the regulation of B cell activation and selection.
Development of high-affinity IgG responses is determined by the activity of the CD23-FcγRIIb pathway. Engagement of CD23 by sialylated IgG immune complexes upregulates FcγRIIb expression on B cells, which in turn raises the threshold for the B-cell receptor (BCR)-mediated signaling and B-cell selection. Upon CD23 engagement, only B cells with high-affinity BCRs are selected due to the higher levels of FcγRIIb[20,28].