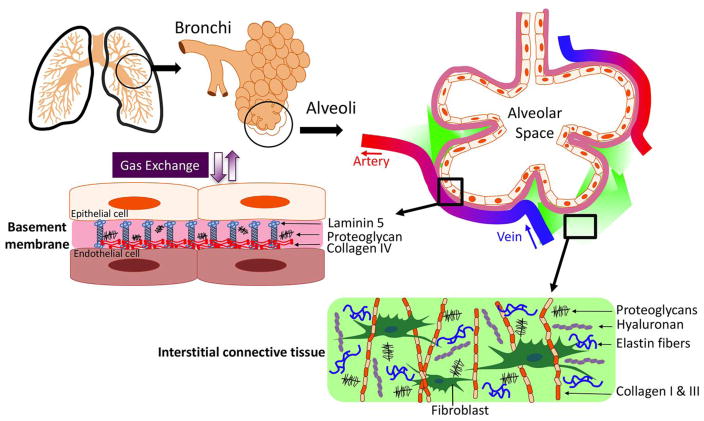
Figure 1. Composition and Distribution of lung ECM.
The ECM basement membrane matrix is composed of nonfibrillar collagens, laminin, and proteoglycans that support many vital physiological lung function. In the proximal airway, basement membrane ECM is dense, while the distal alveoli have an ultrathin basement membrane that aids in effective gas exchange. The lung’s interstitial connective tissue provides necessary elastic properties and tensile strength and is composed of complex networks of fibrous proteins (fibrillar collagen and elastin) as well as hyaluronan and proteoglycans. Excessive accumulation or degradation of ECM molecules within the interstitial matrix is thought to underlie the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases like emphysema and idiopathic fibrosis.