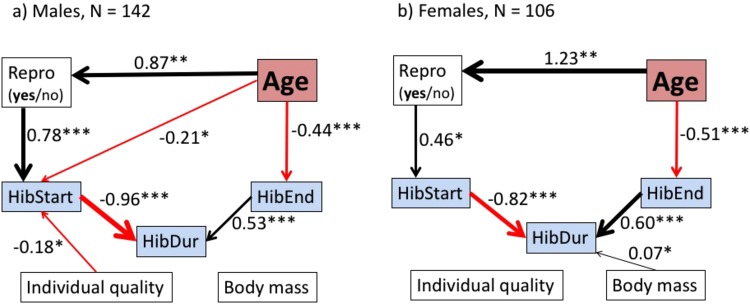
Figure 1.
Path analysis of effects of age on reproduction on hibernation in Glis glis. The path analysis based on piecewise structured equation models for (a) males and (b) females. Boxes represent measured variables (red = age, blue = variables related to hibernation) and can appear as response variables in one path or as a predictor variable in another. For clarity, the binomial variable “sexually active” (Repro: yes/no) is also printed in one box. The impact of age on HibStart (hibernation onset) was partly indirect and caused by sexual activity. Arrows represent unidirectional relationships among variables (black = positive effect, red = negative effect). Shown are all included fixed variables, but only significant (P < 0.05) effects are represented by an arrow (for more details, i.e. non-significant effects see Supplementary information S1). The thickness of each significant path arrow has been scaled on the magnitude of the standardized regression coefficient. Asterisks indicate the significance level: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, marginal and conditional R2 are given in the text (see also Supplementary information S2). HibStart = onset of hibernation (day of year), HibDur = hibernation duration (d), HibEnd = end of hibernation (day of year), Age = log (age) in years, repro = sexually active yes/no (for details see Material and Methods), Individual quality = lifespan of the individual (years), Body mass was measured in g prior to hibernation.