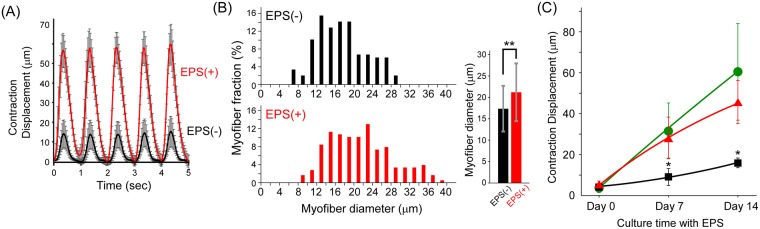
Figure 5.
Effect of EPS-induced continuous contraction on maturation of myofiber sheets. (A) Contraction displacement of myofiber sheets cultured with no stimulation for 10 days (EPS(−)) and with no stimulation for 7 days and then continuous stimulation for 3 days (EPS(+)). Continuous EPS (voltage: 10 V, frequency: 1 Hz, duration: 3 ms) was applied for 1 h with 3 h rest. This procedure started at day 7 after induction of differentiation and was repeated for 3 days. To compare their contraction abilities, EPS was applied at 1 Hz frequency for 5 seconds. (n = 3) (B) Distribution and average value of myofiber diameters with and without continuous EPS for 2 weeks. The data were summarized from three myofiber sheets for each group (total number of myofibers: more than 150). (**P < 0.01) (C) Effect of continuous EPS on contractile ability of myofiber sheets for 2 weeks. Two different continuous EPS (triangle: 3 ms, circle: 10 ms) were applied for 1 h with 3 h rest. This procedure started at day 7 after induction of differentiation (Day 0 for EPS exercise) and was repeated for 2 weeks (Day 14). As the control, myofiber sheets were cultured without continuous EPS (square). The displacements of the shortening myofibers were monitored at Day 0, 7, and 14. (n = 5) (*P < 0.05 vs other samples at the same time point).