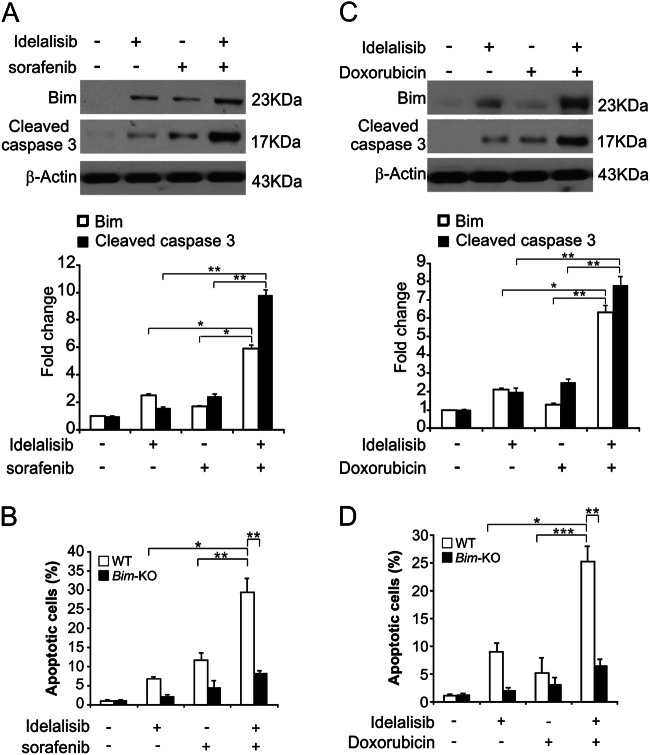
Fig. 5. Idelalisib synergizes with sorafenib or doxorubicin to induce apoptosis via Bim in HCC.
a HepG2 cells were treated with 2.5 μmol/L idelalisib, 5 μmol/L sorafenib, or their combination for 24 h. Bim and Cleaved-caspase 3 expression were analyzed by western blotting and normalized to β-actin. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test). b WT and Bim-KO HepG2 cells were treated 2.5 μmol/L idelalisib, 10 μmol/L sorafenib, or their combination for 24 h. Apoptosis was analyzed by a nuclear fragmentation assay. The results were expressed as the means ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 (Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test). c HepG2 cells were treated with 2.5 μmol/L idelalisib, 5 μmol/L doxorubicin, or their combination for 24 h. Bim and Cleaved-caspase 3 expression were analyzed by western blotting and normalized to β-actin. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test). d WT and Bim-KO HepG2 cells were treated 2.5 μmol/L idelalisib, 5 μmol/L doxorubicin, or their combination for 24 h. Apoptosis was analyzed by a nuclear fragmentation assay. The results were expressed as the means ± SD of three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001**P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 (Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test)