Figure 5.
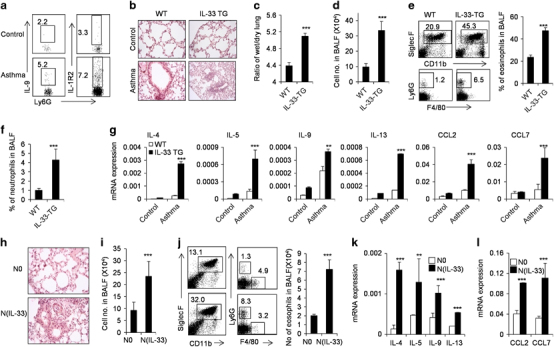
N(IL-33) neutrophils promote OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation in vivo. OVA-presensitized WT and IL-33-TG mice were challenged with aerosolized OVA daily for 3 days as described in the Materials and methods section. (a) IL-9+ and IL-1R2+ neutrophils in BAL fluid of wild-type asthma mice were detected by flow cytometry. (b) H&E staining of lung tissues from control or OVA-induced asthma WT and IL-33-TG mice is presented. (c) Ratio of wet/dry lung weights of WT and IL-33-TG mice after OVA challenge was measured as described in the Materials and methods section. (d) Cell numbers in BAL fluid of WT and IL-33-TG mice after OVA challenge. (e) Flow cytometric analysis of infiltrated cells such as eosinophils in BAL fluid of WT and IL-33-TG mice after OVA challenge. (f) Proportion of neutrophils in BAL fluid of WT and IL-33-TG mice after OVA challenge is presented. (g) The mRNA expression levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, CCL2 and CCL7 in lung tissues of WT and IL-33-TG mice after OVA challenge were detected by real-time PCR. (h) Wild-type neutrophils were stimulated with IL-33, and N0 or N(IL-33) cells were transferred into OVA-presensitized syngeneic wild-type recipients before challenged with aerosolized OVA for 3 days as described in the Materials and methods section. H&E staining of lung tissues from mice treated as described. (i) Cell numbers in BAL fluid of OVA-induced asthma mice transferred with N0 and N(IL-33) cells. (j) The infiltrated cells in BAL fluid of asthma mice treated with N0 and N(IL-33) cells were detected by flow cytometry. Eosinophil numbers in BAL fluid were presented. (k and l) Quantitative PCR analysis of IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, CCL2 and CCL7 expression levels in lung tissues of asthma mice treated with N0 and N(IL-33) cells. Data are expressed as mean±s.d. (n=3–5) and are one representative of the three independent experiments with similar results. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with control mice. BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; CCL, C-C motif chemokine ligand; H&E, hematoylin and eosin; IL, interleukin; OVA, ovalbumin; WT, wild type.
