Figure 1.
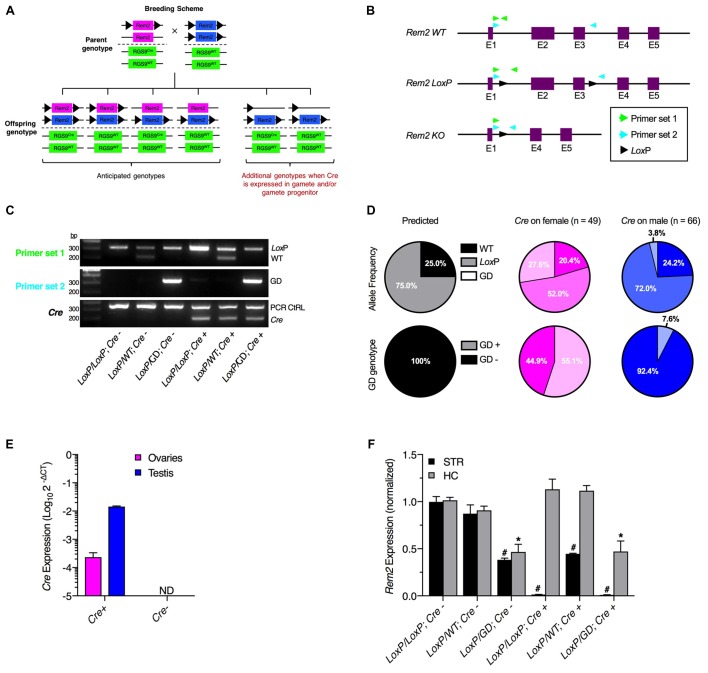
Germline recombination of Rem2 conditional alleles by Rgs9cre driver mice. (A) Summary of anticipated and observed genotypes. (B) Schematic of Rem2 gene showing the wildtype allele, conditional allele with LoxP sequences flanking exons two and three, and knockout allele following Cre-recombinase (Cre) dependent deletion. Two primer sets were used to distinguish the three alleles. Primer set one flanked the 5′ LoxP site, while primer set two flanked the entire floxed region. Note that the complementary DNA sequence for the reverse primer of Primer set 1 is excised following recombination, which results in failed polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. (C) PCR results from genomic DNA (gDNA) purified from ear biopsies. PCR using primer set 1 produced two possible amplicons corresponding to the wildtype (221 bp) and LoxP conditional (327 bp) alleles. PCR with primer set 2 resulted in three possible amplicons corresponding to the wildtype (1,915 bp; not shown), LoxP conditional (2,065 bp; not shown), and Cre-dependent deleted (338 bp) alleles. The Cre PCR reaction contained primers within the Cre coding sequence (200 bp) and PCR control primers (350 bp). (D) Allele frequency and germline genotype frequency predicted for the cross, Rem2LoxP/LoxPRgs9WT/WT × Rem2LoxP/WTRgs9Cre/WT, and observed frequencies when the Cre gene was inherited from the female or male parent. (E) RT-qPCR from gonad cDNA showing Cre expression in Cre+ mice. (F) RT-qPCR from striatum and hippocampus cDNA showing nonconditional Rem2 knockout. #p < 0.05 compared to LoxP/LoxP; Cre-STR; *p < 0.05 compared to LoxP/LoxP; Cre-HC. GD, germline deletion. ND, not detected.