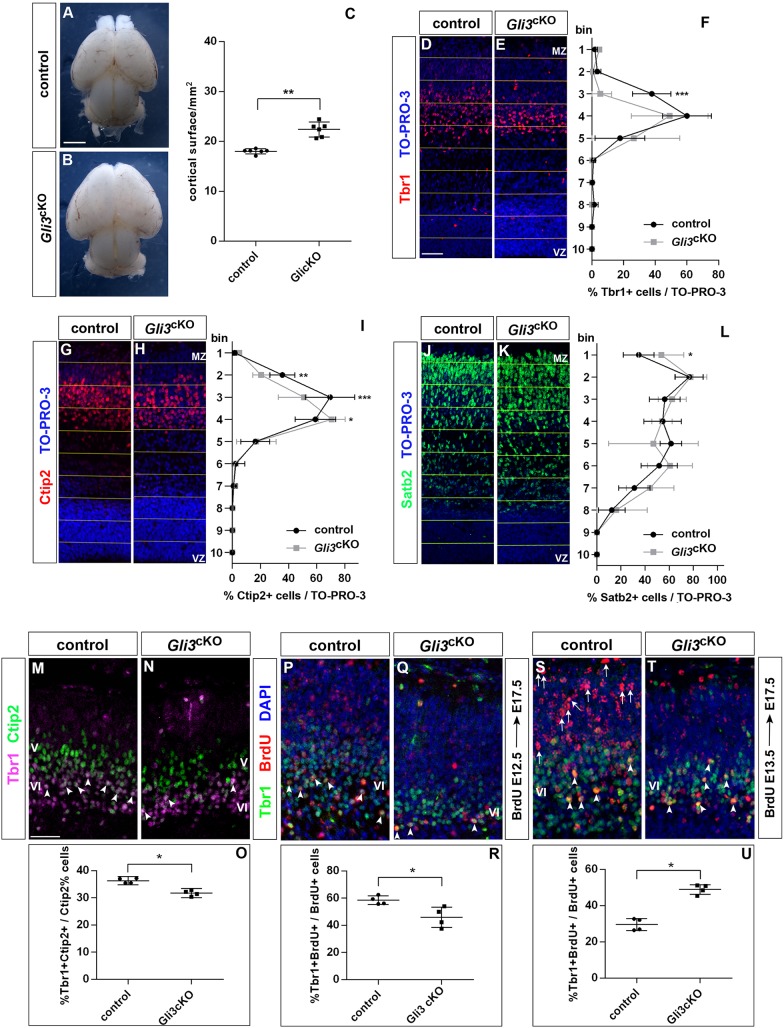
Fig. 3.
Gli3 conditional inactivation affects cortical size and architecture. (A,B) Dorsal views of E18.5 control (A) and Gli3cKO (B) brains. Gli3cKO embryos only form a small olfactory bulb-like structure in the rostral telencephalon, which is not visible in this dorsal view (Amaniti et al., 2015). (C) Graph comparing the surface area of control and Gli3cKO cerebral cortices. (D-L) Immunohistochemistry on E17.5 control and Gli3cKO brains using the indicated antibodies. (D-F) Tbr1+ neurons occupy a reduced area in the deep cortical plate of the Gli3cKO cortex. (G-I) Ctip2+ neurons occupy deeper positions in the cortical plate of Gli3cKO embryos. (J-L) Distribution of Satb2+ upper layer neurons, which have not completed their migration at this stage. (M-O) Tbr1 and Ctip2 double immunofluorescence on coronal sections of E17.5 brains showed that the relative position of Tbr1+ layer VI and Ctip2+ layer V neurons is maintained in Gli3cKO embryos. Moreover, the proportion of Tbr1+Ctip2+ double positive neurons (arrowheads) is reduced in the mutant (O). (P-U) The formation of Tbr1+ neurons is delayed in Gli3cKO embryos. (P-R) The proportion of Tbr1+ neurons born at E12.5 (arrowheads) is reduced in Gli3cKO embryos. (S-U) BrdU birthdating at E13.5 showed an increase in BrdU+Tbr1+ neurons (arrowheads) in Gli3cKO embryos. Note the large number of BrdU+Tbr1− neurons (arrows) superficial to the Tbr1 domain in control embryos. All statistical data are presented as mean±95% CI; n=6 (A-C) and n=4 (D-U); *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.005; Mann–Whitney test (C,O,R,U) and two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test (F,I,L). MZ, marginal zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bars: in A, 2 mm for A,B; in D,M, 50 µm for D,E,G,H,J,K,M,N,P,Q,S,T.