Figure 3.
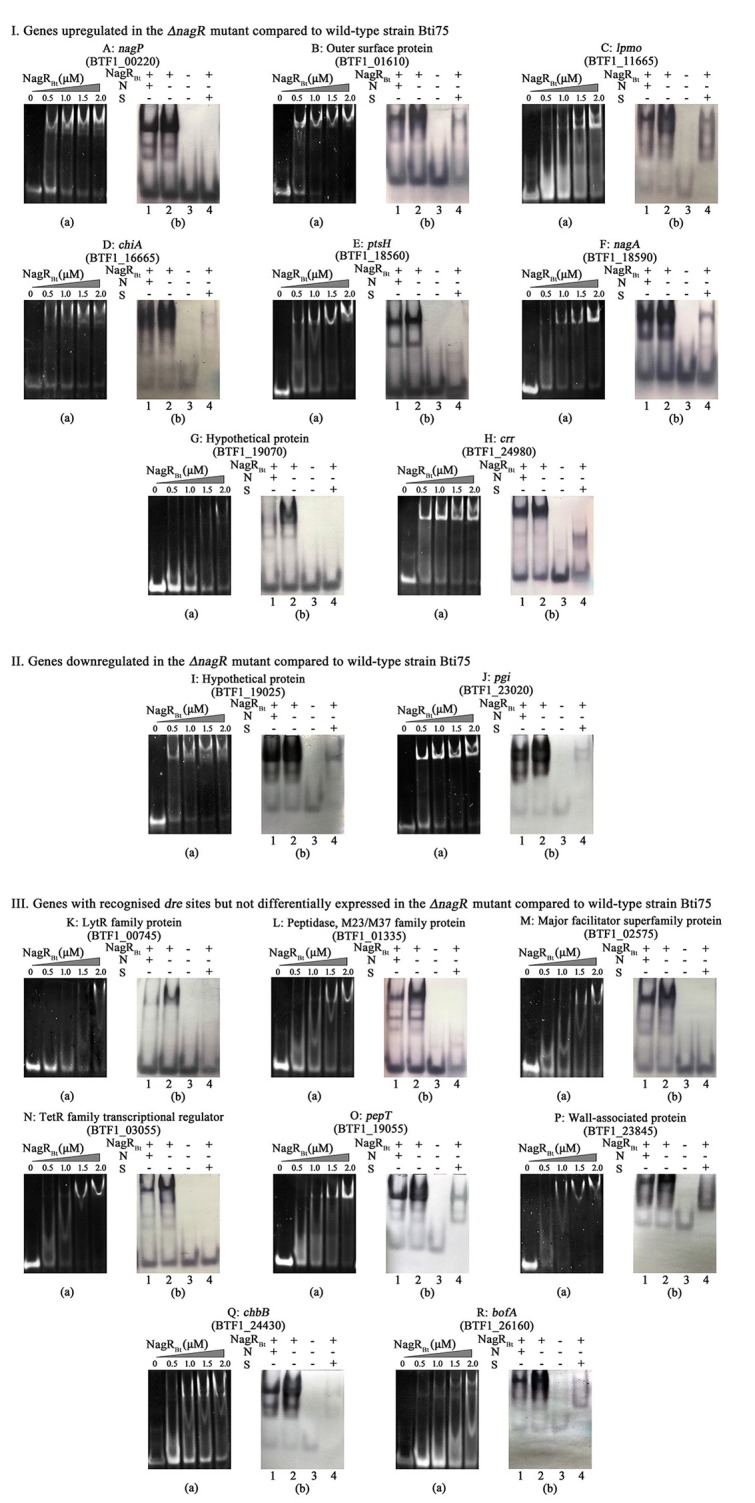
NagRBt-binding sites are detected by EMSAs. (I) Genes upregulated in the ΔnagR mutant compared to wild-type strain Bti75; (II) Genes downregulated in the ΔnagR mutant compared to wild-type strain Bti75; (III) Genes with recognized dre sites but not differentially expressed in the ΔnagR mutant compared to wild-type strain Bti75. (a): Each 0.2 μM 40 bp-Pdre was electrophoresed after incubation with various concentrations of NagRBt. (b): EMSAs to determine the specific binding of NagRBt. Lane 1, Pdre (Bio), NagRBt, and 0.5 μg/μL salmon sperm DNA for non-specific competitor (N); Lane 2, Pdre (Bio), NagRBt; Lane 3, Pdre (Bio); Lane 4, Pdre (Bio), NagRBt, and a 400-fold excess of unlabeled Pdre for specific competitor (S). All the non-specific and specific competition assays used 3.0 μM NagRBt and 0.2 μM Pdre (Bio). Different letters represent different genes. A: nagP, BTF1_00220; B: outer surface protein, BTF1_01610; C: lpmo, BTF1_11665; D: chiA, BTF1_16665; E: ptsH, BTF1_18560; F: nagA, BTF1_18590; G: hypothetical protein, BTF1_19070; H: crr, BTF1_24980; I: hypothetical protein, BTF1_19025; J: pgi, BTF1_23020; K: lytR family protein, BTF1_00745; L: peptidase, BTF1_01335; M: major facilitator superfamily protein, BTF1_02575; N: TetR family transcriptional regulator, BTF1_03055; O: pepT, BTF1_19055; P: wall-associated protein, BTF1_23845; Q: chbB, BTF1_24430; R: bofA, BTF1_26160.
