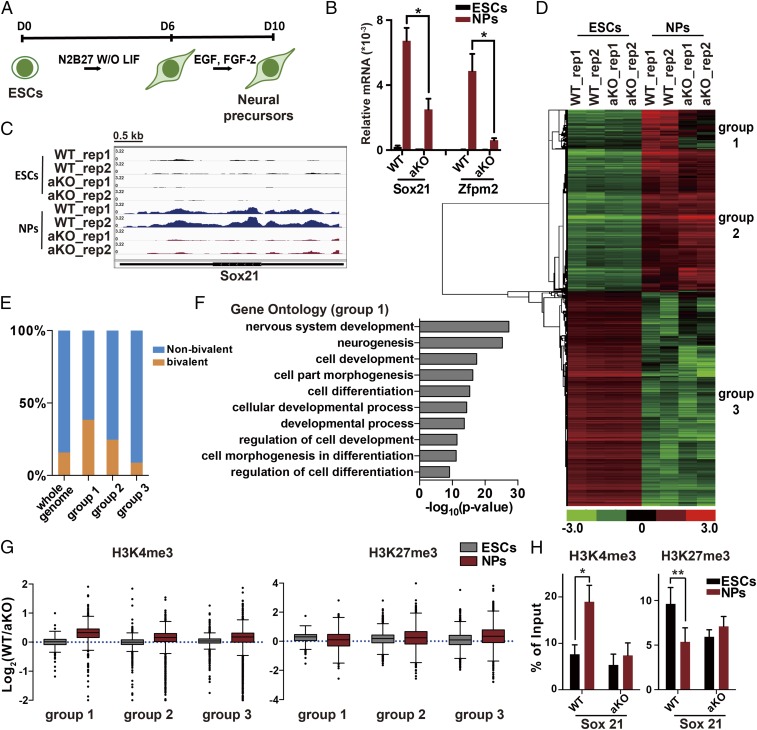
Fig. 4.
Asf1a is required for induction of lineage-specific genes during neural differentiation. (A) An outline of the monolayer ES cell in vitro neural differentiation. (B) Gene-expression analysis of Sox21 and Zfpm2 in Asf1a-KO cells expressing EV (aKO) or WT Asf1a (WT) during neural differentiation using RT-PCR. Data are from three independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. The P value was calculated by using a t test between WT and aKO NPs (*P < 0.05). (C) Snapshot of RNA-seq results at the Sox21 locus. Data are from two independent experiments (rep1 and rep2). (D) The hierarchical clustering analysis of the differentially expressed genes during neural differentiation of WT and aKO cells identified by RNA-seq. (E) The percentage of bivalent genes in each of the three subgroups of genes identified in D. (F) GO analysis of the group 1 genes. The top 10 significant GO terms and P value are displayed. (G) Relative levels of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 between WT and aKO at the promoters of three subgroups of genes identified in D. The y axis represents the log2 ratio of ChIP-seq reads between WT and aKO lines. (H) Analysis of changes in H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 at the gene promoter of Sox21 in WT and aKO lines by ChIP-PCR. The P value was calculated by using a t test between ES cells and NPs (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). Note that Asf1a-KO and WT clones were the same as used in Fig. 5.