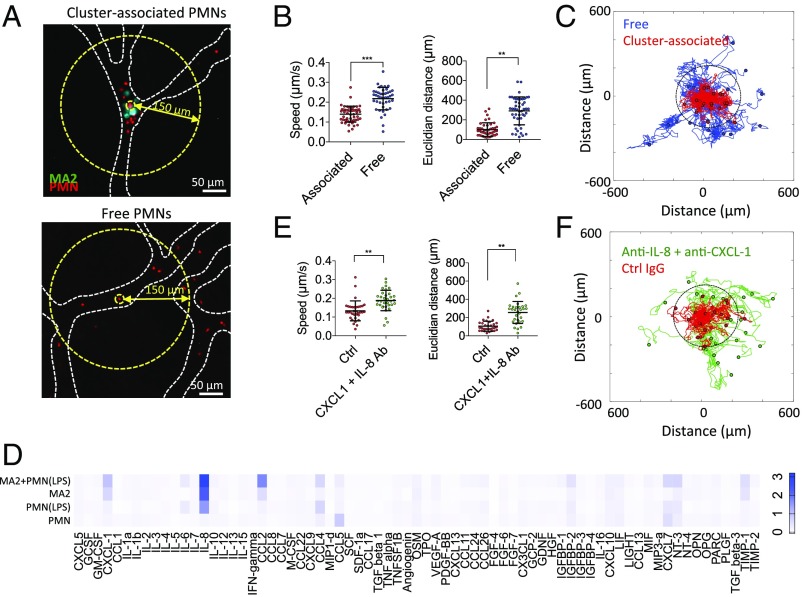
Fig. 2.
Cluster-associated PMNs exhibit migratory confinement that is dependent on autologous chemotaxis to secreted factors. (A) Cluster-associated and free PMNs arrested intraluminally. (B) Migration speeds and end-to-end distance from original position of cluster-associated vs. free PMNs (n = 43–53 PMNs per condition over five devices). (C) Tracks of free (blue) and cluster-associated (red) PMNs over 90 min (40-s time step). Dotted circle delineates the 150-μm radius. (D) Cytokine array showing relative magnitudes of secreted factors from MA2 alone, PMN alone, LPS-activated PMNs, or MA2 + PMN coincubation, after 4 h of culture (two replicates). (E) Migration speed and end-to-end distance from original position of cluster-associated PMNs with or without anti–CXCL-1 + anti–IL-8 (n = 30–34 PMNs per condition, over five devices). Error bars indicate SD, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (F) Migration tracks of cluster-associated PMNs incubated with anti–CXCL-1 + anti–IL-8 or control (Ctrl) IgG.