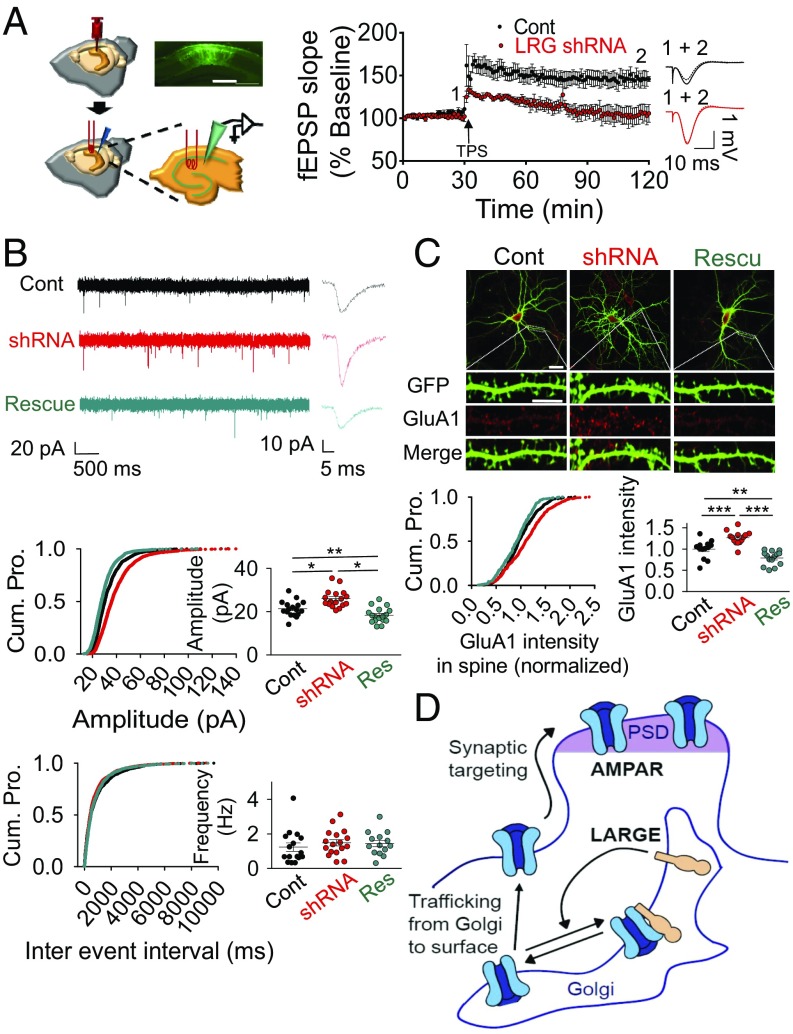
Fig. 3.
LARGE KD causes synaptic AMPA-R overload, and thus impairs in vivo LTP in the hippocampal CA1 region. (A) Schema, plot, and traces from an in vivo LTP analysis after an injection of virus encoding LARGE shRNA. LARGE KD (LRG shRNA) was found to impair LTP (n = 8, eight mice; two-tailed t test: P < 0.05). Cont, control. (Scale bar: 300 μm.) (B) Whole-cell patch clamping yielded current traces, cumulative plots, and scattered plots from mEPSC analysis following transfection with plasmids encoding scrambled shRNA (Cont), LARGE shRNA, or LARGE rescue. LARGE KD increased the amplitude, but not the frequency, of mEPSCs, whereas LARGE rescue reversed this amplitude change. Three different groups from 48 coverslips in four batches of neuronal culture were recorded [n = 1,653, n = 1,660, and n = 1,622 events from n = 17, n = 17, and n = 17 neurons, respectively; Amplitude: *P < 0.001, **P = 0.026; Frequency: P = 0.639; Cont, black; shRNA, red; Rescue (Res), cyan]. Cum. Pro., cumulative probability. (C) LARGE KD (shRNA) increased the number of GluA1 molecules in the dendritic spines, whereas this phenomenon was reversed by LARGE rescue (n = 529, n = 529, and n = 562 spines from n = 13, n = 14, and n = 14 neurons, respectively; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (Scale bars: whole-cell image, 30 μm; dendrite, 10 μm.) In an image of a neuron, the intensity of the GluA1 signal at the spine (synaptic GluA1) was normalized to the intensity of the GluA1 signal at the dendritic shaft (total GluA1). (D) Schema of our working model for the regulation of AMPA-R trafficking by LARGE. PSD, polysynaptic density. (B and C) One-way ANOVA was used.