Figure 1.
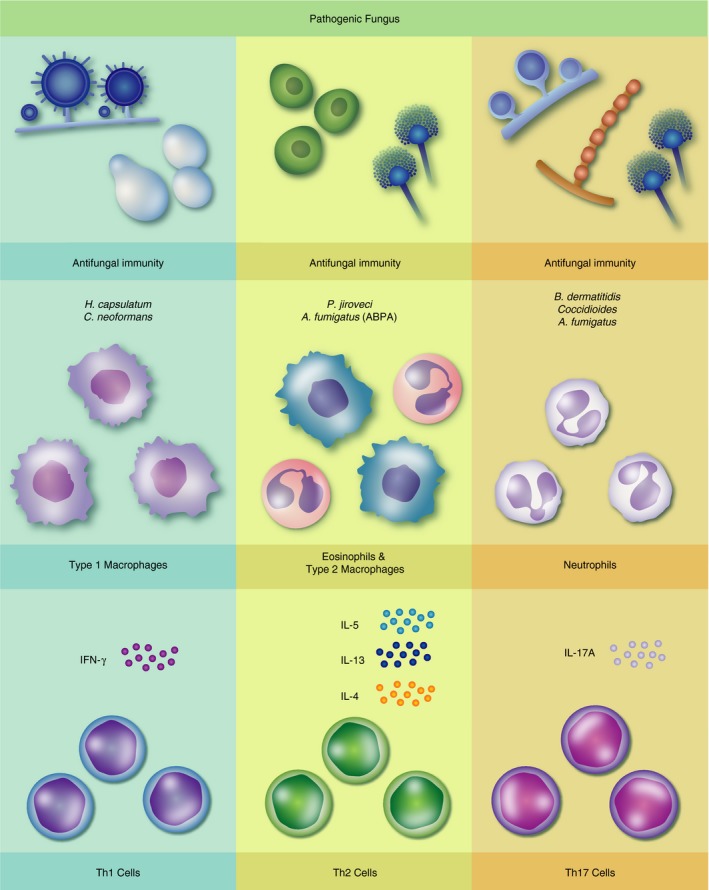
T‐cell responses to pulmonary fungal infections. Left column: Type 1 responses, characterized by interferon‐γ (IFN‐γ) production from CD4 cells and Type 1/classically activated macrophages, mediate antifungal immunity to Histoplasma capsulatum and Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Centreal column: Eosinophil and alternatively activated macrophages supported by interleukin‐4 (IL‐4), IL‐5 and IL‐13 production from T cells protect against Pneumocystis jiroveci infection and drive pathology during allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA). Right column: Host immunity to Blastomyces dermatitidis, Aspergillus fumigatus and Coccidioides species is mediated in part by T helper type 17 cells by IL‐17A and neutrophil‐dependent mechanisms.
