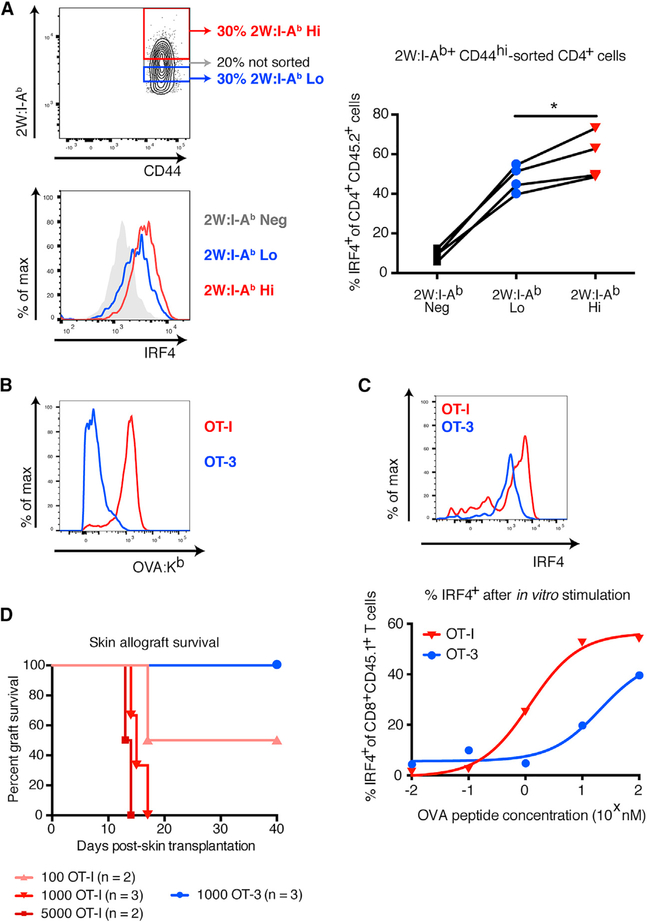
Figure 2. Tetramer Binding Correlates with T Cell Functional Avidity and Capacity to Mediate Skin Allograft Rejection.
(A) Top left: flow cytometry plot of layout to sort populations with differential 2W:I-Ab binding. Bottom left: representative histogram showing levels of IRF4 staining in tetramer-sorted, 2W:I-Ab-specific T cells after in vitro stimulation with 2W peptide. Right: percentage of IRF4+ tetramer-sorted, 2W:I-Ab-specific T cells after in vitro stimulation with 2W peptide. (B) Histograms showing intensity of OVA:Kb pentamer binding in OT-I/RAG-KO and OT-3/TCRα-KO T cells 7 days after immunization with 2W-mOVA DST. (C) Top: representative histogram showing levels of IRF4 staining in OT-I/RAG-KO and OT-3/TCRα-KO T cells after in vitro stimulation with 10 nM SIINFEKL peptide. Bottom: percentage of IRF4+ cells within the population of CD8+ CD45.1+ OT-I/RAG-KO and OT-3/ TCRα-KO T cells after in vitro stimulation with a dose titration of SIINFEKL peptide. Lines indicate nonlinear regression analysis. (D)Survival of B6 2W-mOVA skin allografts in P14/RAG-KO recipients adoptively transferred with sorted OT-I/RAG-KO or OT-3/TCRα-KO T cells (p < 0.05 by log rank test). Data in (A) were analyzed by one-way paired ANOVA. *p < 0.05. See also Figure S3.