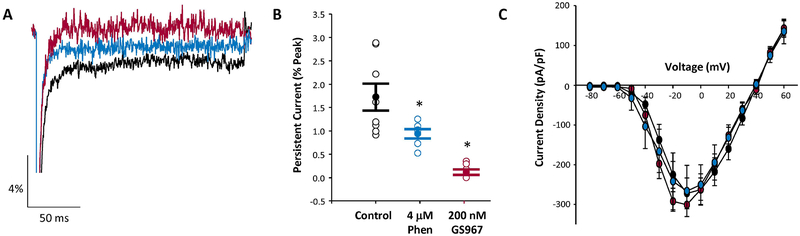
Figure 1.
GS967 inhibits persistent sodium current in acutely isolated hippocampal pyramidal neurons from Scn8aD/+ mice. A, Representative traces showing persistent sodium current of untreated (black), GS967 treated (red), and phenytoin (PHT) treated (blue) neurons from Scn8aD/+ mice. B&C, Summary data of persistent sodium current (B) and current-voltage relationship for peak sodium current (C) for untreated (black symbols, n = 8), phenytoin treated (blue symbols, n = 6), and GS967 treated (red symbols, n = 7) neurons from Scn8aD/+ mice. Open symbols represent individual cells, while closed symbols represent mean ± S.E.M. Statistical comparison were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test. * represent statistical difference compared to untreated cells for phenytoin (p < 0.04 and GS967 (p < 0.001) treated cells.