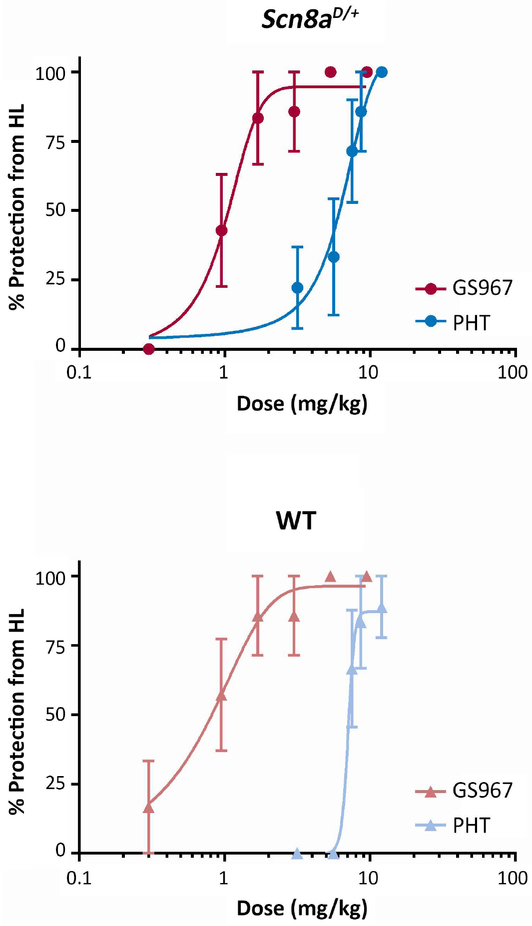
Figure 3.
GS967 protects against MES-induced seizures in Scn8aD/+ and wild-type (WT) mice with greater potency than phenytoin (PHT). Mice were pre-treated with test compound or vehicle and then received an electroconvulsive stimulus determined to reliably elicit seizures with maximal hindlimb extension in Scn8aD/+ (120 mC) or WT (720 mC) mice. A, Dose response curves of GS967 and phenytoin for MES seizures in Scn8aD/+ mice. The curve for GS967 is significantly shifted compared to phenytoin and the estimated EC50 for GS967 and phenytoin are 1.1 ± 0.23 mg/kg and 5.33 ± 0.69 mg/kg, respectively (p < 0.001, n = 5–24, Student’s t-test). Symbols represent mean ± S.E.M. B, Dose response curves of GS967 and phenytoin for MES seizures in WT mice. The curve is also significantly shifted and the estimated EC50 for GS967 and phenytoin are 0.70 ± 0.22 mg/kg and 6.93 ± 0.45 mg/kg, respectively (p < 0.001, n = 6–26, Student’s t-test).