Fig. 1.
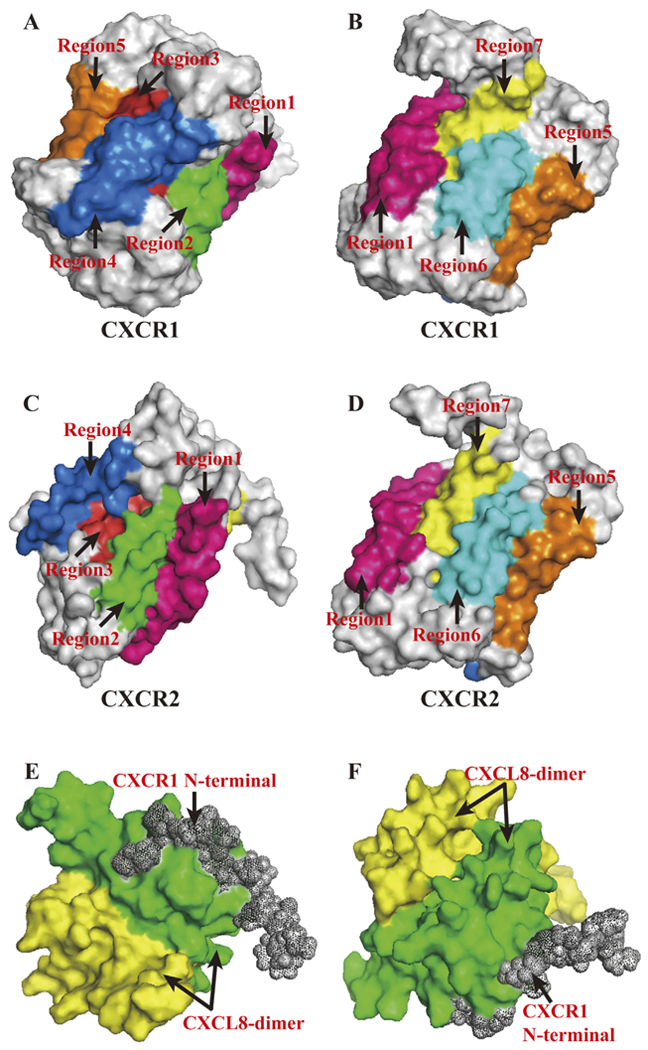
PyMOL Molecular Graphics System was used to present above structures. (A, B). Corresponding transmembrane regions within CXCR1 tertiary structure. Regions marked in different colours with arrows showed its seven transmembrane domains. Simulation of tertiary structure was constructed using PDB lefiof 2LNL produced by Park et al. [17]. (C, D). Corresponding transmembrane regions within CXCR2 tertiary structure. Regions marked in different colours with arrows showed its seven transmembrane domains. The amino acid sequence of CXCR2, NCBI RefSeq NP_0015481, were used to model CXCR2 tertiary structure in Swiss Model [155]. (E, F). Interaction model between CXCL8-dimer and CXCR1 N-terminal. Simulation of tertiary structure was constructed using PDB le of 1ILP produced by Skeltonfiet al. [16].
