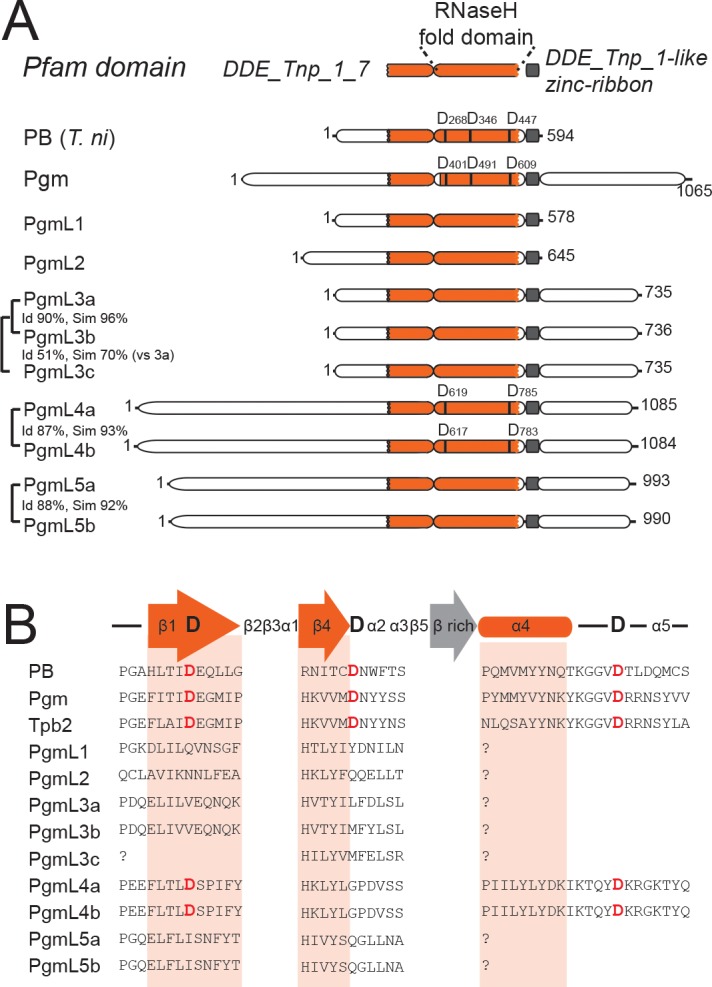
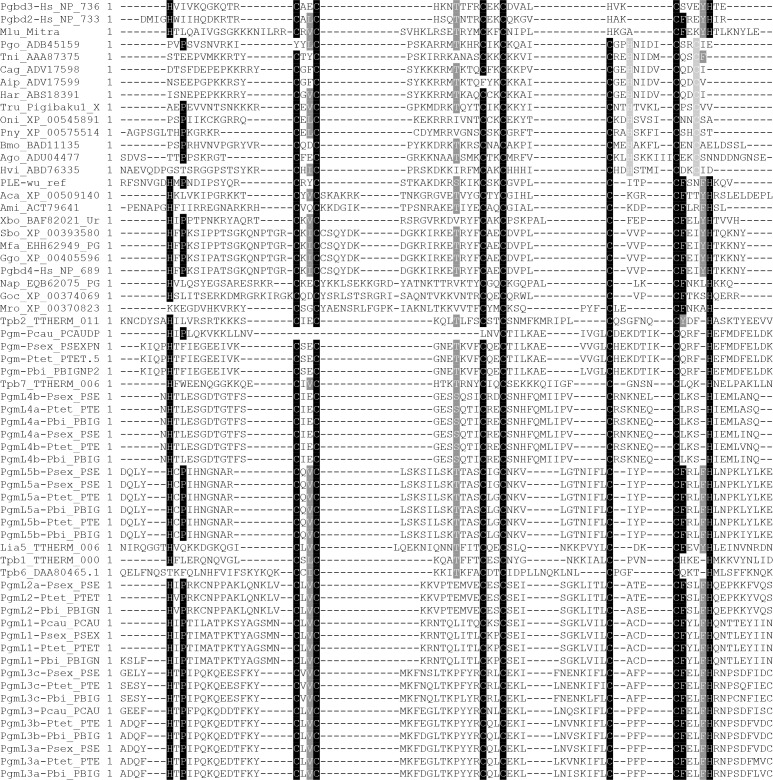
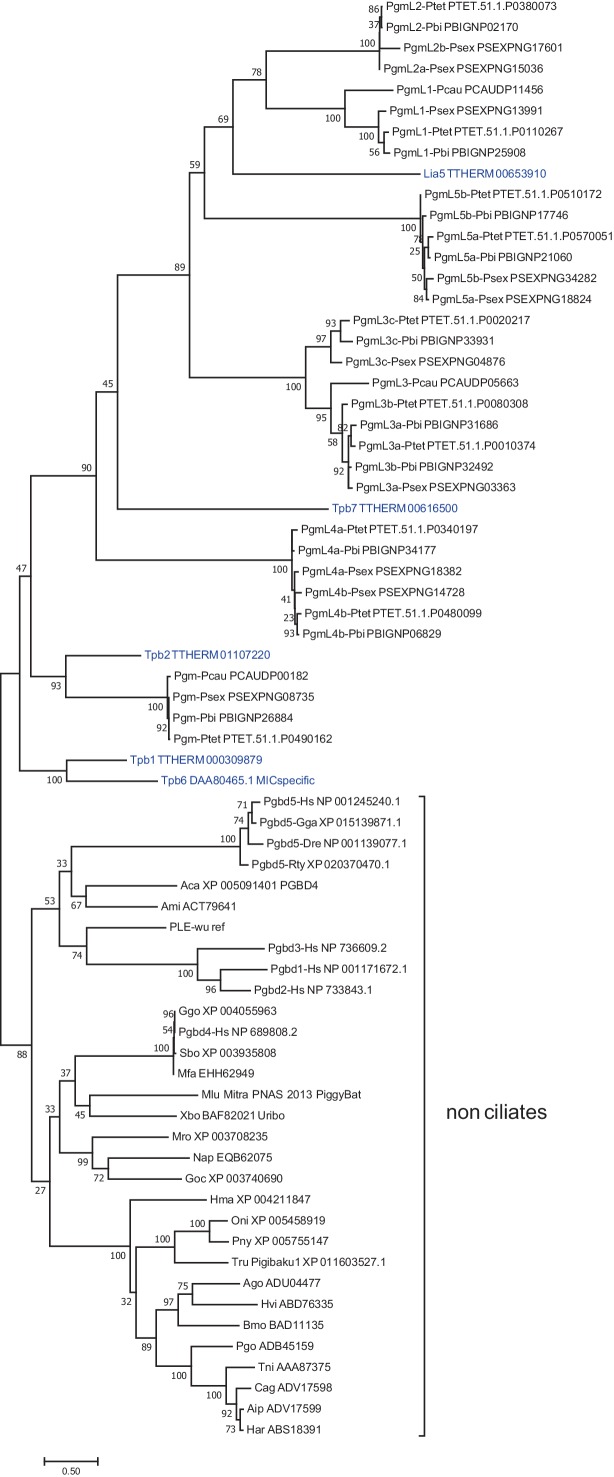
Figure 1. Novel domesticated PiggyBac transposases in Paramecium.
(A) Domain organization of the PiggyBac transposase (PB) from T. ni and of Paramecium PiggyBac-related proteins (Pgm and PgmLs). The Pfam domain DDE_Tnp_1_7 is shown as a bipartite orange domain, with the RNase H fold corresponding to its right part (conserved catalytic D residues are indicated by vertical bars). The DDE_Tnp_1-like zinc ribbon is in grey. Id: % of amino acid identity; sim: % of similarity. (B) Protein sequence alignment of the residues surrounding the three catalytic aspartic acids (DDD). Following secondary structure prediction, sequence alignments were adjusted manually, using the expected position of the three catalytic D residues in the first and fourth β strands and immediately downstream of the fourth α helix of the RNase H fold domain, respectively (Hickman et al., 2010). ‘?' indicates that the expected α4 helix could not be predicted using the PSIPRED secondary structure prediction software.