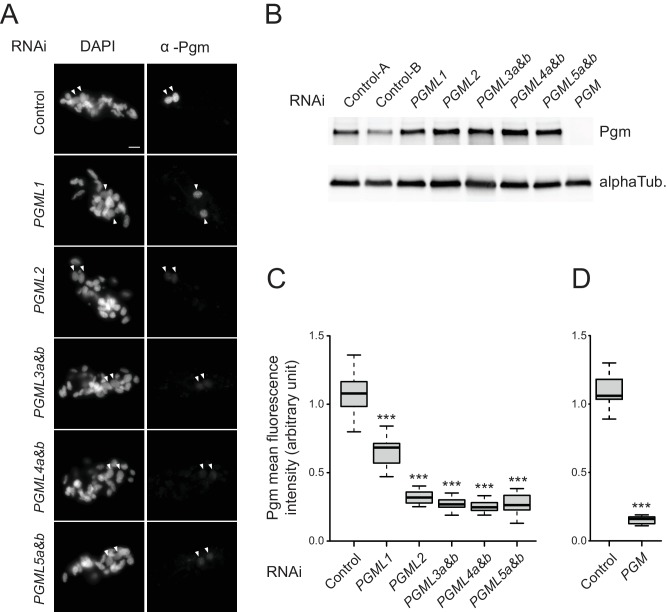
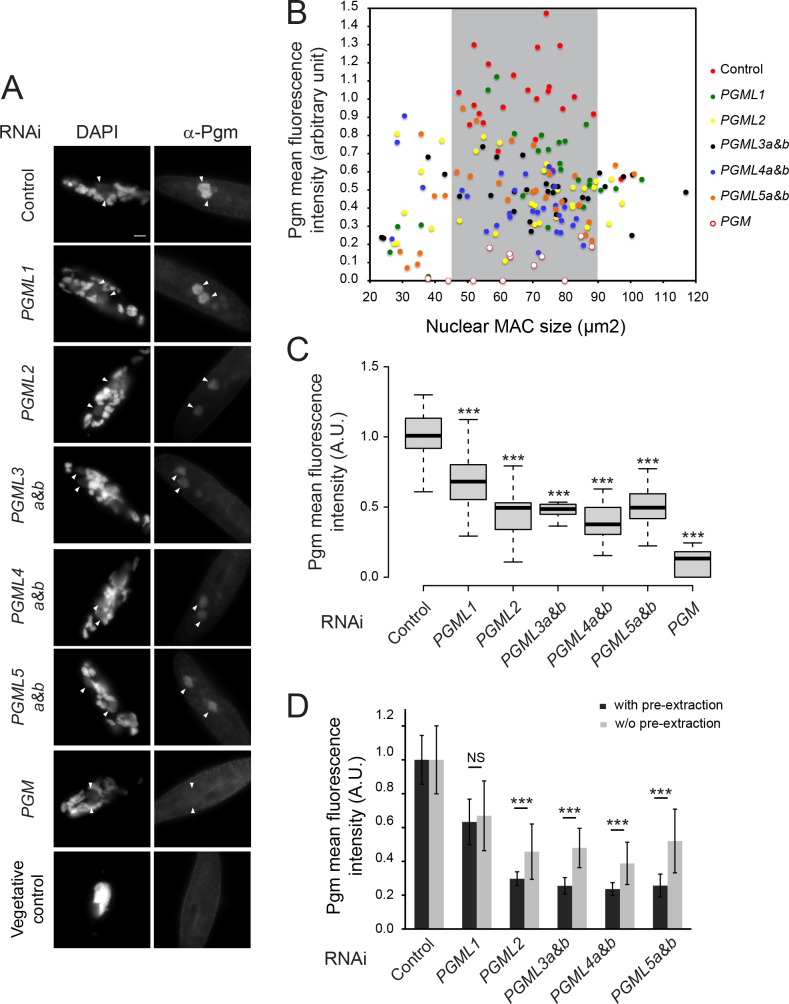
Figure 4. Expression and localization of Pgm in PGML KDs.
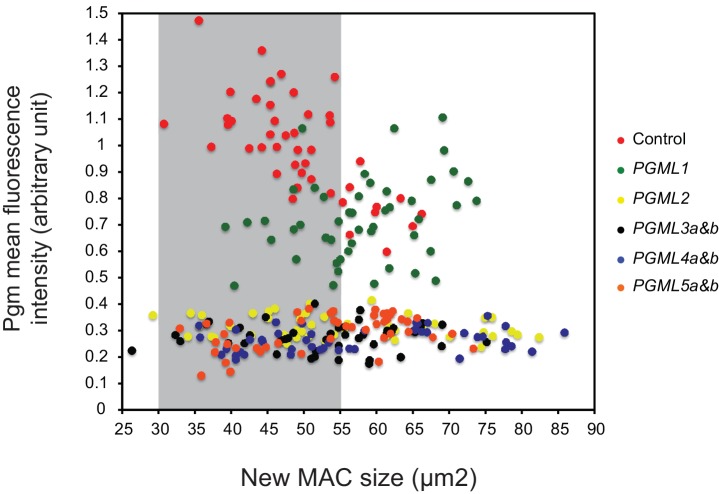
(A) Immunostaining of Pgm in early autogamous cells subjected to control (L4440) or PGML RNAi. Developing MACs are indicated by white arrowheads. Scale bar is 10 μm. (B) Western blot analysis of Pgm expression in early autogamous cells subjected to control (L4440: two independent controls A and B are shown), PGML or PGM RNAi. (C) Boxplot representation of the distribution of Pgm fluorescence intensities quantified in 30–55 μm2 developing MACs subjected to the different RNAi shown in (A). This size window corresponds to the maximal Pgm signal in the control (Figure 4—figure supplement 1) and was chosen to quantify nuclear Pgm immunofluorescence for all KDs, since no significant size difference was noticed for developing MACs relative to the control. For each condition, 19 to 35 developing MACs were analyzed. (D) Independent set of experiments showing the quantification of Pgm fluorescence intensity in 30–55 μm2 developing MACs following control (ND7) or PGM RNAi. 11 and 12 MACs were analyzed, respectively. In (C) and (D): *** for p<0.001 in a Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon statistical test (see Materials and methods for details).