Figure 3.
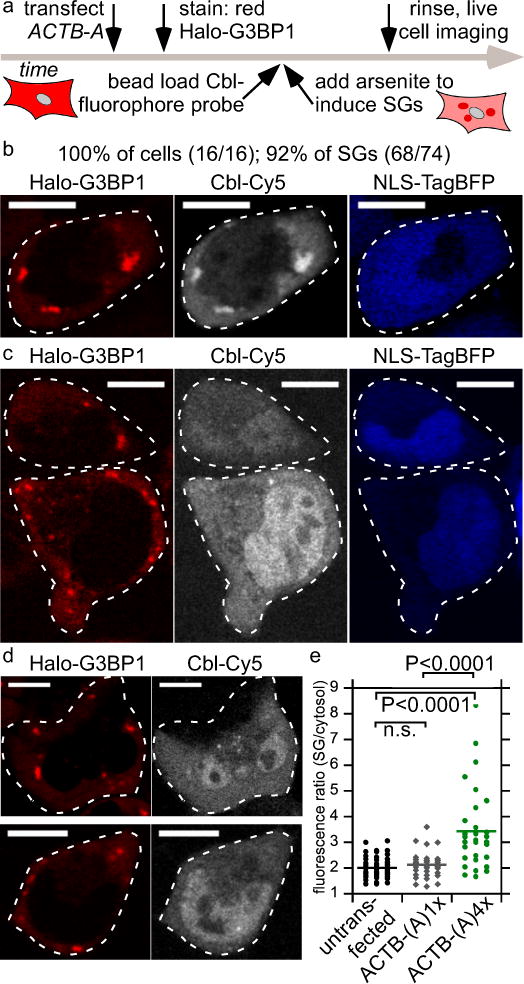
Monitoring ACTB mRNA localization to stress granules (SG) via Cbl-fluorophore probe binding to the RNA tag A. (a) Experimental strategy of labeling the Halo-tagged G3BP1 SG marker protein with the red fluorescent JF585 dye, followed by bead loading the Cbl-fluorophore probe, induction of SGs by arsenite for 30-45 min and live cell imaging. (b) U2-OS cells producing Halo-G3BP1 were transfected with ACTB-(A)4x and the transfection marker TagBFP. 24 h post transfection, cells were stained with the JF585 Halo dye. Shown is a representative live cell to assess colocalization of the SG marker protein Halo-G3BP1 and ACTB mRNA (3 independent experiments, 16 cells, 74 SGs). At least one SG was visible in all 16 cells (100%) and 92% of SGs were detectable. (c) The same experiment as in (b) was performed, except that ACTB-(A)1x was transfected (3 independent experiments, 14 cells, 30 SGs). Two representative live cells are presented. In 43% of the cells at least one SG was detectable and 40% of all SGs were detected in the Cbl-Cy5 channel. (d) The same experiment as in (b) was performed, except that ACTB-(A)4x was not transfected (2 independent experiments, 39 cells, 100 SGs). Two representative live cells are presented. In 38% of the cells at least one SG was detectable and 32% of all SGs were visible in the Cbl-Cy5 channel. (e) Quantification of fluorescence signal accumulation in representative SGs (line represents mean). Scale bar = 10 μm. One way ANOVA (95% confidence limit), post hoc test (Tukey HSD).
