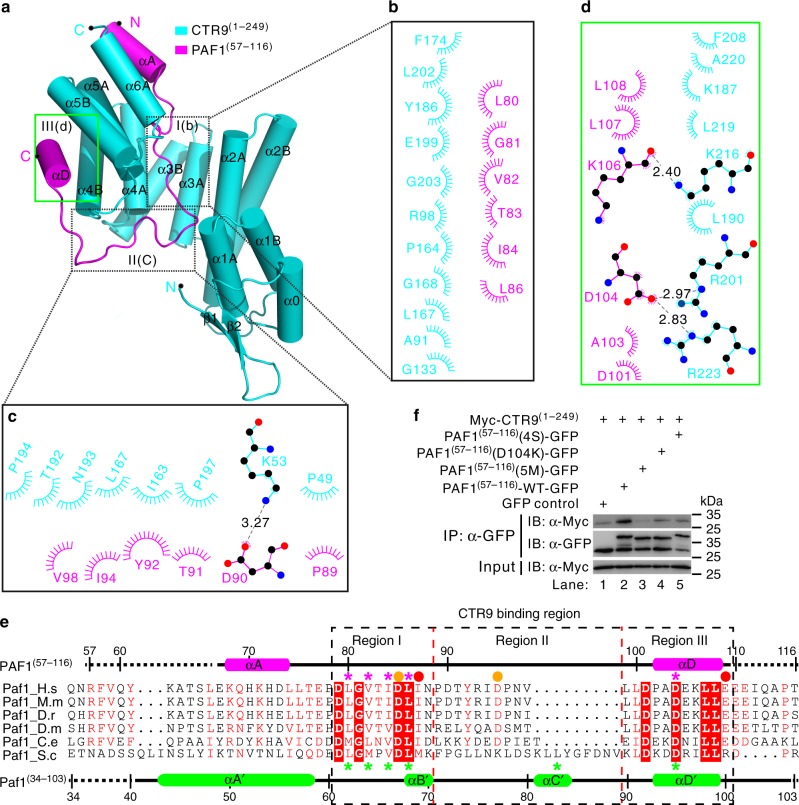
Fig. 2.
The interaction interface of the human CTR9/PAF1 heterodimer. a–e The CTR9(1–249)/PAF1(57–116) interface is divided into three regions corresponding to the CTR9 TPR1–5 concave channel/N-terminal loop of PAF1 (b, e), the side of the TPR1–5/C-terminal loop of PAF1 (c, e), and the convex surface of the TPR4–5/αD helix of PAF1 (d, e). The interaction details between CTR9 and PAF1 in the three regions are shown in (b) to (d). Charge–charge or hydrogen-bonding and hydrophobic interactions are shown as gray dotted lines and spoked arcs, respectively. e Structural-based sequence alignment of the CTR9-binding fragments of PAF1 in various species. In this alignment, the secondary structures of human PAF1 and yeast Paf1 are shown at the top and bottom, respectively, according to the crystal structures of CTR9(1–249)–PAF1(57–116) and Ctr9(1–313)–Paf1(34–103), and conserved residues are shaded in red. The highly conserved residues, which are mutated in PAF1(57–116)(4S), PAF1(57–116)(D104K), or PAF1(57–116)(5M) and the Paf1(4S), Paf1(L83S) or Paf1(D95K) construct, are indicated with magenta and green asterisks, respectively. The disease-associated amino acid substitutions I87M or E109K (category 1 shown in Fig. 3a) and D85N or D95Y (category 2 shown in Fig. 3a) are indicated with red and orange spheres, respectively. Three regions of CTR9-binding in PAF1 are indicated with dotted boxes. Species abbreviations: H.s, Homo sapiens; M.m, Mus musculus; D.r, Danio rerio; D.m, Drosophila melanogaster; C.e, Caenorhabditis elegans; S.c, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. f Co-IP experiments testing the interaction between CTR9(1–249) and PAF1(57–116) wild-type (WT) or mutants. The PAF1(57–116)(4S) mutant contains four amino acid substitutions L80S, V82S, I84S, and L86S. The PAF1(57–116)(5M) mutant contains five amino acid substitutions L80S, V82S, I84S, L86S, and D104K. Myc was tagged to the N-terminal of CTR9(1–249) and GFP was tagged to the C-terminal of PAF1(57–116) WT or mutant. Extracts were prepared from HEK293T cells transfected with various combinations of plasmids, as indicated. The bottom panel shows 3% of the Myc fusion proteins for each IP. Uncropped blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8