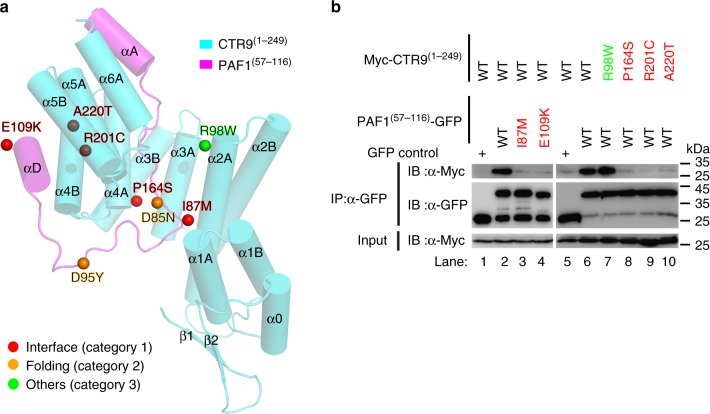
Fig. 3.
Disease-associated mutations affect the interaction between CTR9 and PAF1. a Disease-associated mutations in the CTR9(1–129)/PAF1(57–116) complex. For clarify, only five missense-mutation sites in category 1 (interface), two sites in category 2 (folding) of PAF1, and one site (R98W) in category 3 (others) of CTR9 are highlighted with spheres and colored in red, orange, and green, respectively. The full lists of disease-associated mutations in CTR9 and PAF1 are summarized in Supplementary Tables 2 and 3, respectively. b The interaction sites between CTR9(1–249) and PAF1(57–116) containing various disease-associated mutations were evaluated using a co-IP strategy. Myc was tagged to the N-terminal of CTR9(1–249) WT or mutant and GFP was tagged to the C-terminal of PAF1(57–116) WT or mutant. Extracts were prepared from HEK293T cells transfected with various combinations of plasmids, as indicated. The bottom panel shows 3% of the Myc fusion proteins for each IP. Uncropped blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8