Figure 9.
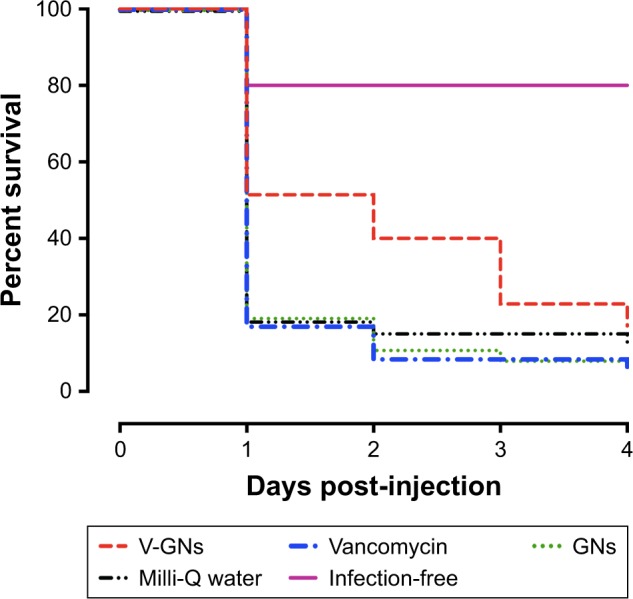
Percent survival (%) of S. aureus-infected zebrafish larvae receiving different treatments, monitored from the day of injection until 4 days post-injection. The median dose of S. aureus assessed directly after injection in control larvae was 3,200 CFU per larva. The infected larvae were treated with vancomycin-loaded gelatin nanospheres (V-GNs), free vancomycin, or only gelatin nanospheres (GNs). Injection of Milli-Q water was used as mock treatment. Larvae receiving two injections of Milli-Q water (infection-free) were used as controls for the injection procedure. The group size of infected larvae was between 32 and 35 larvae per group at the start of the experiment. The group size of infection-free larvae was 10 larvae. Survival of zebrafish larvae receiving locally delivered vancomycin (V-GNs) was statistically significantly higher than survival of zebrafish larvae receiving systemically delivered vancomycin (P=0.01).
Abbreviation: CFU, colony-forming unit.
