FIGURE 2.
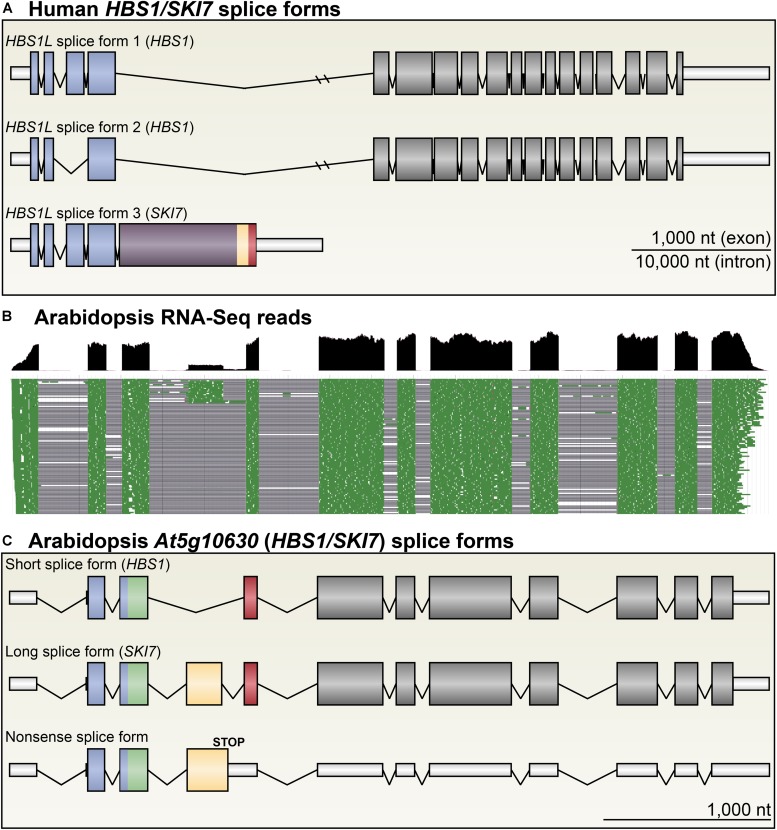
Arabidopsis HBS1/SKI7 is alternatively spliced. (A) The human HBS1/SKI7 locus, called HBS1L, produces three primary splice forms: HBS1L splice form 1, a long splice form with 18 exons; HBS1L splice form 2, a slightly shorter splice form skipping exon 3; and HBS1L splice form 3, which selects an alternative exon 5 followed by transcription termination. HBS1Lv3 includes sequences that promote interaction of the protein with the RNA exosome (yellow and red; see Figure 4A). (B) RNA-Seq of light-grown seedlings shows that At5g10630 is alternatively spliced into three major splice forms (Cheng et al., 2017). Cumulative RNA-Seq reads are shown in black (top panel), and select individual aligned reads are shown in green (bottom panel), with spliced sequences indicated by a black line. Note that reads for the fourth exon are ∼20% of the level of reads for the other coding sequence exons. (C) At5g10630 forms three major splice forms. A short splice form (top) skips exon 4 (yellow), yielding a transcript that encodes HBS1 (A). A long splice form (middle) includes exon 4 (yellow), yielding a transcript that encodes SKI7 (A). Rarely, an alternative acceptor site is selected for exon 4, adding five amino acids with no apparently functional consequence. A nonsense splice form (bottom) retains intron 4, which includes two codons, yielding a transcript that is likely subject to NMD. Exons are colored to match protein models in subsequent figures; UTRs are indicated with narrow, white bars.