FIGURE 1.
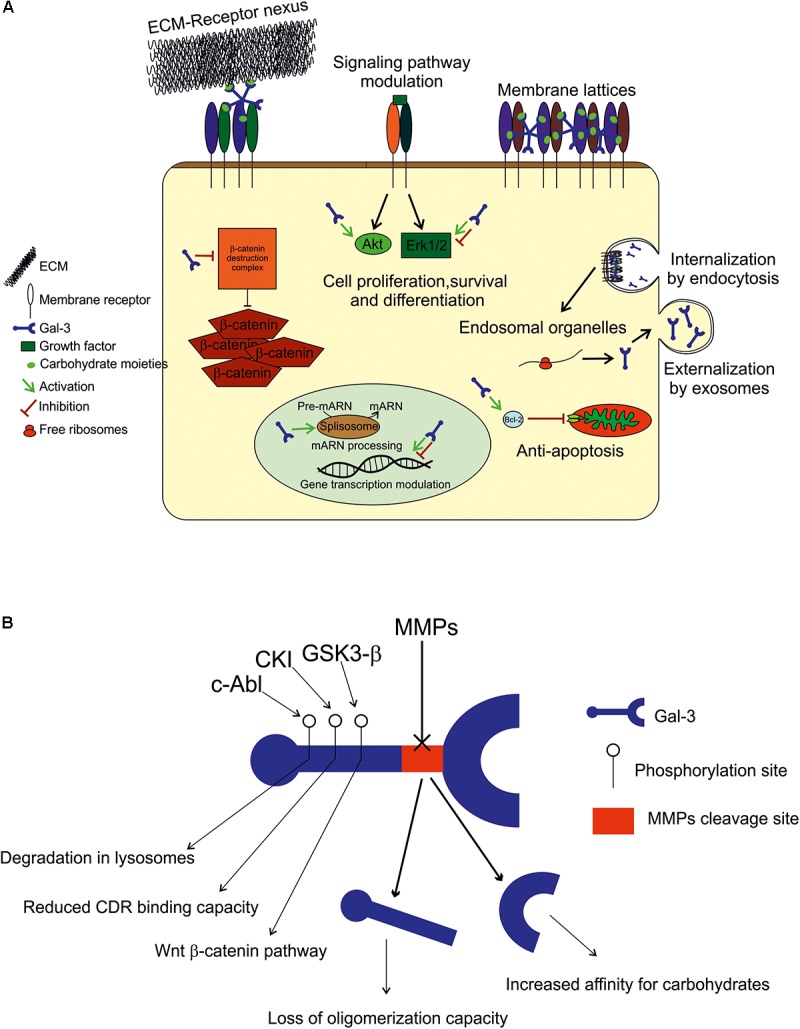
(A) Extracellular space: Gal-3 either binds to the ECM compounds (laminin, hensin, elastin, collagen IV, tenascin-C and -R, and integrin) to modulate cell adhesion, or interacts with plasmatic membrane receptors by binding to carbohydrate moieties in an autocrine or paracrine fashion to form membrane lattices and trigger intracellular events. Intracellular space: within the cell, Gal-3 is found in both cytoplasm and nucleus, and its binding appears to be mediated by protein-protein interactions. In the cytoplasm, it plays an anti-apoptotic role (Bcl-2), and modulates signaling pathways (Akt and in Erk 1/2) to promote or inhibit cell growth, proliferation and differentiation. In the nucleus, Gal-3 is crucial for pre-mRNA splicing (spliceosome incorporation) and to promote or repress transcription. Internalization and secretion: Gal-3 enters the cell by non-clathrin-mediated endocytosis and goes through endosomal organelles to be later sorted elsewhere or degraded. Gal-3 is secreted via a non-classical pathway and apparently through exosomes. (B) Regulation: Gal-3 activity is regulated by MMP2 and MMP9 cleavage (Ala62 to Tyr63), generating a 22 kDa whole CRD peptide (high affinity for carbohydrates) and a 9 kDa N-terminal peptide (oligomerization capacity). Also, Gal-3 is phosphorylated in Tyr residues by c-Abl kinase to promote its own degradation in lysosomes in Ser residues by casein kinase I to reduce its carbohydrate binding capacity, and by GSK3-β to regulate the Wnt-β-catenin pathway.
