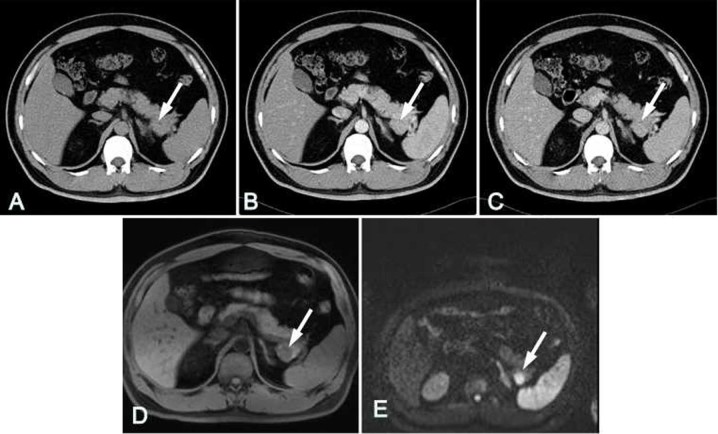
Figure 4.
Case 1. A 56-year-old male was confirmed to have IPAS by surgical pathology. (A) The unenhanced CT image exhibited only slight enlargement of the pancreatic tail. In the (B) arterial phase and (C) delayed phase, similar attenuation levels were observed for the IPAS (arrow) and the surrounding pancreatic tissue. (D) In T1-weighted imaging, the IPAS exhibited a low signal in the pancreatic tissues (arrow). (E) In diffusion-weighted imaging using a high b-value (600 sec/mm2), the lesion (arrow) clearly had higher signal intensity than the pancreas. IPAS, intrapancreaticaccessory spleen; CT, computed tomography.