Figure 3.
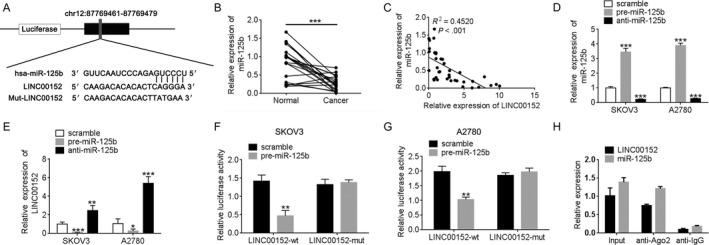
Identification of miR‐125b as a target of LINC00152. A, Alignment of potential LINC00152 sequences with miR‐125b as identified by miRcode (http://www.mircode.org). B, qRT‐PCR was performed to detect the expression of miR‐125b in paired normal and ovarian cancer tissues (n = 20). C, The correlation between theLINC00152 expression level and miR‐125b level was measured in 20 ovarian cancer tissues (P < .001). D, miR‐125b is downregulated and overexpression in SKOV3 and A2780cells compared to control groups as determined by qRT‐PCR. The expression of miR‐125b was normalized to U6. E, The expression of LINC00152 was upregulated after silencing miR‐125b in SKOV3 and A2780 cells. F,G, The relative luciferase activities were inhibited in the SKOV3 (F) and A2780 (G) cells cotransfected with wild‐type LINC00152 vector and pre‐miR‐125b, and not with the mutant‐type vector. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase. H, Association of LINC00152 and miR‐125b with Ago2 in SKOV3 cells. Cellular lysates from SKOV3 cells were used for RIP with antibody against Ago2. LINC00152 and miR‐125b expression levels were detected using qRT‐PCR. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments, *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001
