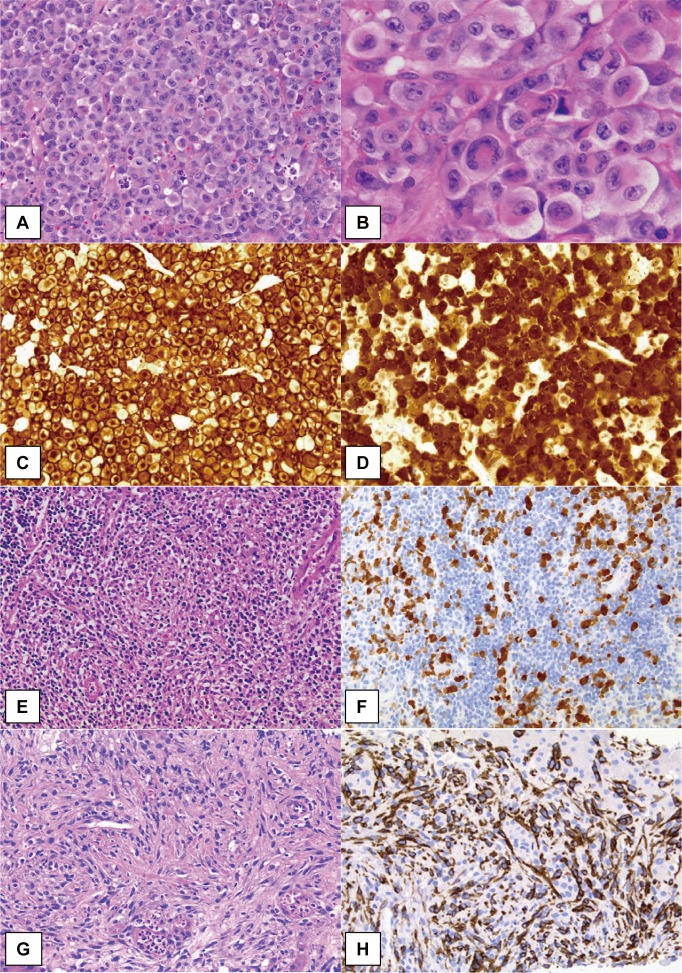
Fig. 1.
Morphological patterns and immunostaining of ALK-positive ALCL.
The common pattern of ALK-positive ALCL comprises sheets of large, “hallmark” cell proliferation. Neoplastic cells exhibit variably shaped nuclei; invaginated, horseshoe- or kidney-shaped, donut-like, or Reed-Sternberg-like nuclei with abundant cytoplasm (A, B). Strong immunoreactivity for CD30 is generally observed both on the membrane and in the Golgi regions (C). In cases of ALCL with the t(2;5) translocation, as shown in this figure, the ALK protein has both nucleolar and cytoplasmic staining pattern (E, F). The lymphohistiocytic pattern of ALCL shows conspicuous infiltration of small lymphocytes and histiocytes with pale cytoplasm. Morphologically, neoplastic cells are not clear but are highlighted by ALK immunostaining (F). The sarcomatoid pattern of ALCL is characterized by atypical spindle-shaped cell proliferation with fascicular arrangement, simulating soft tissue sarcomas. Neoplastic cells are positive for CD30 (H) and ALK expression (G, H).