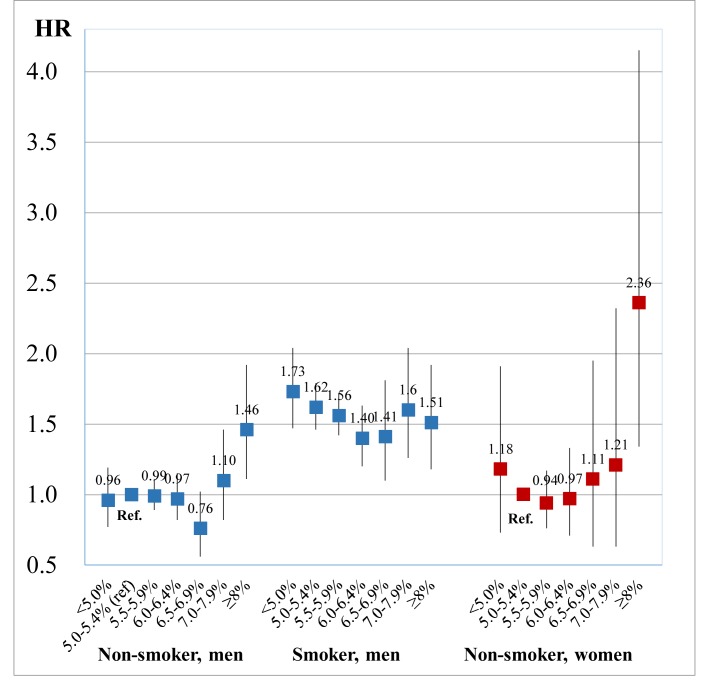
Figure 1.
The association between haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and hearing impairment of high frequency stratified by smoking status. Results obtained by multivariable Cox regression. The reference value was 5.0%–5.4% of HbA1c in non-smoker. The model was adjusted for age (year, continuous), sex, body mass index (<18.5, 18.5–22.9, 23–29.9 or ≥30.0 kg/m2), alcohol consumption (non-drinker, drinker consuming <1, 1 to <2 or ≥2 go of Japanese sake contains approximately 23 g of ethanol), walking time (<60 or ≥60 min/day), self-reported diabetes, hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or receiving medication) and hyperlipidaemia (triglyceride level ≥150 mg/dL, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level <40 mg/dL or receiving medication).