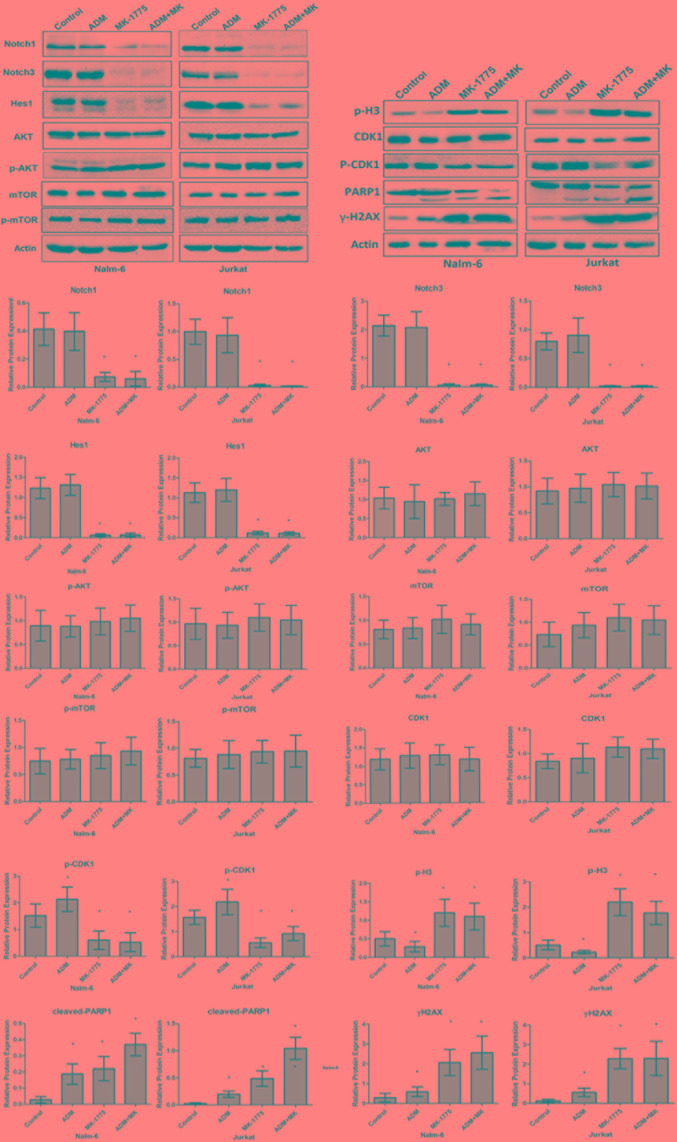
Figure 4.
MK-1775 induced apoptosis due to unscheduled mitotic entry and downregulation of Notch pathway. MK-1775 inhibited the phosphorylation of CDK1, induced apoptosis characterized by cleavage of PARP-1 and increase of γ-H2AX expression. Notch1 ICN and Notch3 ICN were downregulated, but mTOR levels were not altered by MK-1775 treatment. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. β-actin protein served as a protein loading control. *P<0.05 vs. control. ADM, doxorubicin; CDK1, cyclin-dependent kinase 1; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; ICN, intracellular domain; p, phosphorylated; Hes1, hairy and enhancer of split-1; Akt, RAC-alpha serine/threonine protein kinase; p-H3, phosphorylated histone H3; PARP1, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; rH2AX, H2A histone family, member X.