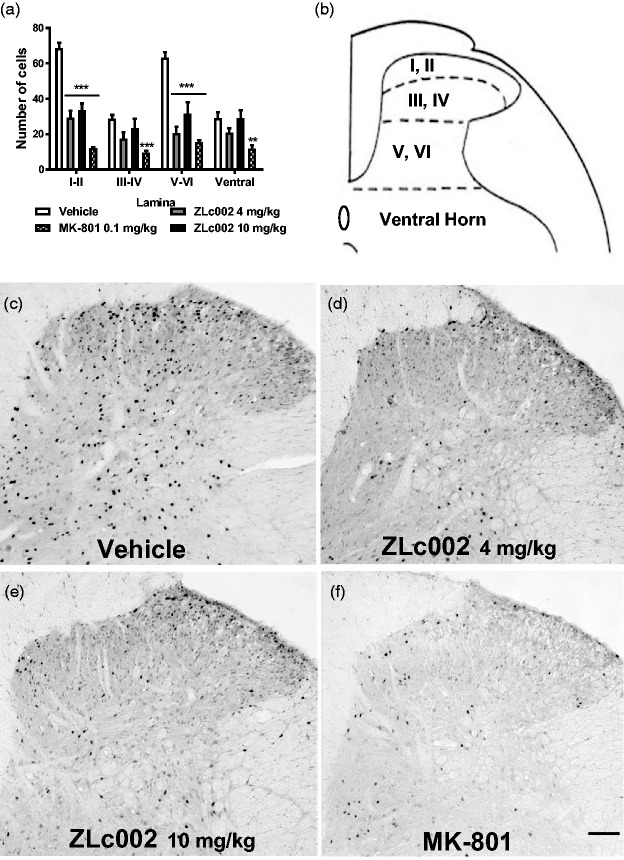
Figure 6.
(a) ZLc002 (4 and 10 mg/kg i.p.) reduced formalin-evoked Fos-like immunoreactivity in laminae I-II (p < 0.001) and laminae V-VI (p < 0.001) relative to vehicle. MK-801 reduced formalin-evoked Fos-like immunoreactivity in laminae I-II (p < 0.001), laminae III-IV (p < 0.001), V-VI (p < 0.001), and the ventral horn (p < 0.01) relative to rats treated with vehicle. (b) Schematic adapted from the rat brain atlas of Paxinos and Watson35 showing spinal cord laminae quantified for Fos-like immunoreactivity. Data are mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5–6 per group) ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle (two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). MK-801 and vehicle groups were published previously but run and processed concurrently with ZLc002-treated groups shown here (see methods and Carey et al.6). Example photomicrographs taken at 10x magnification showing formalin-evoked Fos-like immunoreactivity in lumbar dorsal horn of rats treated with vehicle (c), ZLc002 (4 mg/kg i.p.) (d), ZLc002 (10 mg/kg i.p.) (e), and MK-801 (0.1 mg/kg) (f). Scale bar is equal to 100 µm.