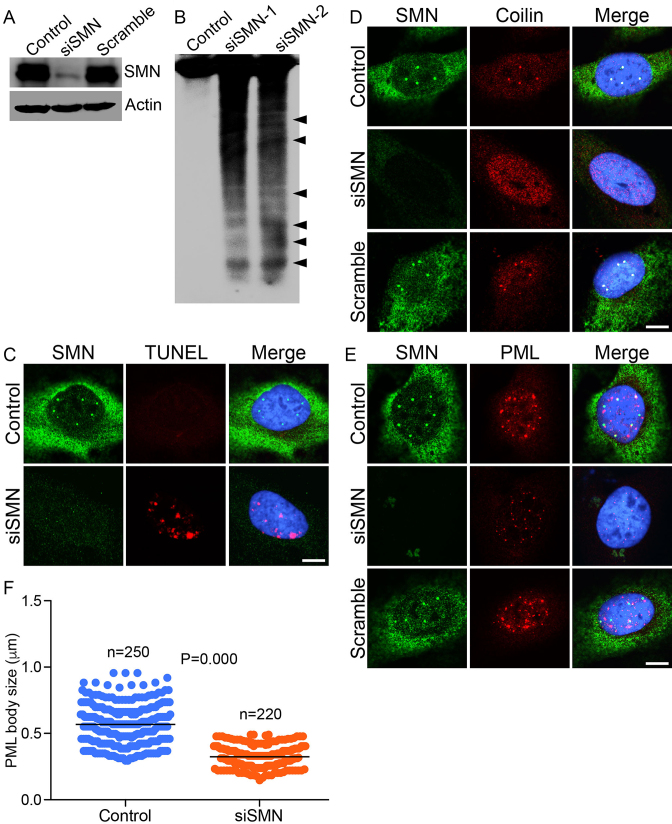
Figure 1.
Acute SMN deficiency (knockdown) causes DNA damage in non-SMA dividing cells. HeLa cells were untransfected (Control) or transfected with siRNA (100 nM) against SMN1 (siSMN) or scrambled siRNA sequence (Scramble) and incubated for 30 h. Cells were harvested to extract proteins and genomic DNA and fixed for staining with antibodies for IF analysis. (A) IB analysis of SMN and β-actin proteins in Control, siSMN and Scramble-treated cells. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from cells untransfected (Control) or transfected with siRNA, 100 nM (siSMN-1) and 200 nM (siSMN-2). Genomic DNA was isolated from Control and siRNA transfected cells (siSMN), 3′-end-labeled with biotin, separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, blotted to Zeta probe blotting membrane and detected using streptavidin–HRP-conjugated chemiluminescence kit. (C) Control and HeLa cells transfected with siRNA (siSMN) and scrambled siRNA (Scramble) were fixed and labeled with modified dUTP (EdU) nucleotide to detect strand breaks by TUNEL staining (red) and SMN is stained in green. Acute SMN deficiency causes disruption of sub-nuclear bodies known to contribute to genomic stability. (D) SMN (green) and coilin, marker of CB (red), (E) SMN (green) and PML, a marker of PML bodies (red). (F) Quantitation of number and size of PML bodies in control and siSMN-treated cells (10 cells/group). The average size of PML bodies in control is 0.55 ± 0.013 microns (n = 250) and in siSMN-treated cells is 0.32 ± 0.001 microns (n = 220). Immunofluorescence of stained cells was examined by confocal microscopy. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar is 10 μm.