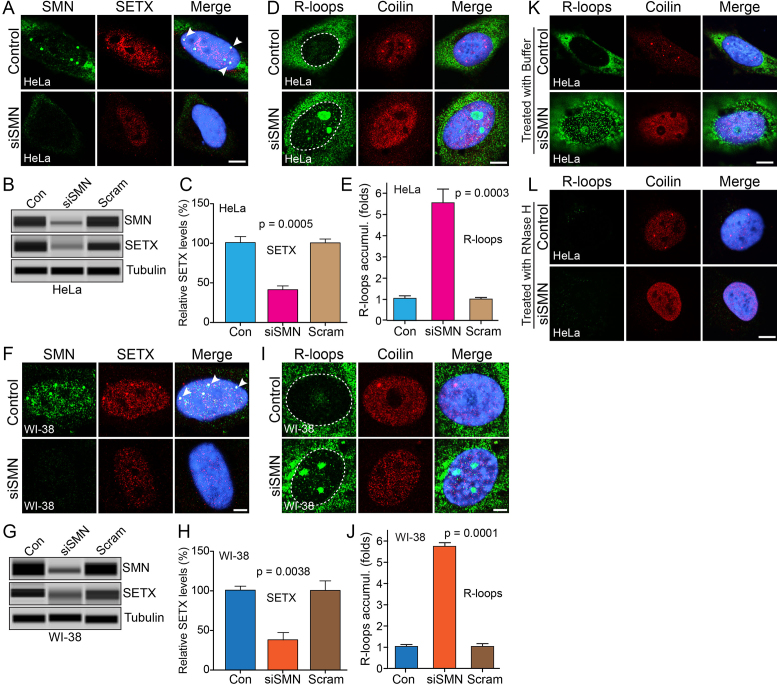
Figure 3.
Acute SMN deficiency causes downregulation of SETX and accumulation of RNA–DNA hybrids (R-loops) in non-SMA dividing human cells. HeLa and WI-38 cells were untransfected (Control) or transfected with siRNA (100 nM) against SMN1 (siSMN) or scrambled siRNA sequence (Scramble) and incubated for 30 h. (A) Immunofluorescence analysis show that SMN (green) and SETX (red) colocalize in sub-nuclear foci of (Control, arrowheads) HeLa cells and knockdown of SMN causes reduction in staining of SETX (red) and (B) IBs for SMN, SETX and Tubulin of cell lysates prepared from Control and siSMN and Scramble (Scram)-treated HeLa cells, (C) quantitative (mean ± s.e.m., n = 3) and statistical analysis (one-way ANOVA) of HeLa cells show knockdown of SMN levels to (22.90 ± 6.71%, P = 0.0003) decreased SETX levels to (41.42 ± 4.79%, P = 0.0005) compared to control and scramble (Scram). (D) Accumulation of RNA–DNA hybrids (R-loops) in SMN-deficient cells. R-loops were detected by monoclonal antibody (S9.6) against RNA–DNA hybrids (green). Coilin is a control stained in red. (E) Quantitative and statistical analysis (one-way ANOVA) of R-loop accumulation in cells using IF images and ImageJ software show cells treated with siRNA (siSMN) have increased R-loops 5.55 ± 0.68-fold (P = 0.0003) accumulation compared to Control and Scramble-treated cells. (F) Colocalization of SMN (green) and SETX (red) in nub-nuclear foci of WI-38 cells (Control, arrowheads) and knockdown of SMN causes reduction in staining of SETX (red). (H) IBs for SMN, SETX and Tubulin of cell lysates prepared from Control and siSMN and Scramble (Scram)-treated WI-38 cells, (I) quantitative (mean ± s.e.m., n = 3) and statistical analysis (one-way ANOVA) of WI-38 cells show knockdown of SMN levels to (31.87 ± 8.44%, P = 0.0008) decreased SETX levels to (37.18 ± 9.33%, P = 0.0038) compared to control and scramble (Scram). (G) Accumulation of R-loops (green) in SMN-deficient cells. (J) Quantitative and statistical analysis (one-way ANOVA) of R-loop accumulation in cells using IF images and ImageJ software show cells treated with siRNA (siSMN) have increased R-loops 5.74 ± 0.20-fold (P = 0.0001) accumulation compared to Control and Scramble-treated cells. Digestion of R-loops with the RNase H enzyme, but not buffer alone, reduces R-loop accumulation. R-loops nuclear levels were quantified from three cell culture replicates (30 cells each). Digestion of R-loops with the RNaseH enzyme, but not buffer alone, reduces R-loop accumulation. Cells transfected with siRNA (siSMN) were permeabilized and treated with (K) buffer only and (L) RNase H enzyme for 20 min, washed and fixed with 4% PFA. Cells were stained with antibodies and IF was examined by confocal microscopy; R-loops (green) and coilin (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar is 10 μm. (Full-length blots are included inSupplementary Figure S9).