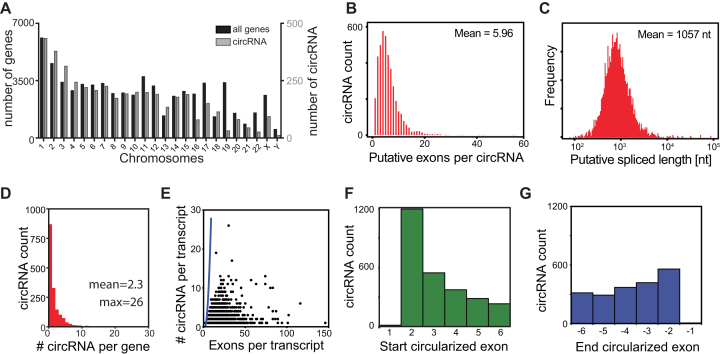
Figure 2.
Characterization of circRNA detected in hematopoietic cells. (A) Distribution of circRNA (in grey) and known genes from hg19/GRCh37 (in black) per chromosome. (B, C) Putative exon usage (B) and maximal putative length (C) of the 4103 circRNA detected in hematopoiesis, as determined by the start and end position of circRNA and splicing annotations of the RNA linear transcript. (D) Number of detected circRNA per gene. (E) Relation between the number of circRNA per transcript and the number of exons of that transcript. Blue line represents the calculated maximum circRNA number per transcript, if all exon combinations were used for circularization. (F, G) Distribution of the first (F) and the last (G) 6 exons used for circularization from the linear RNA in circRNA. 1197/4103 (29.2%) circRNA use the second exon as start exon, and 559/4103 (13.6%) use the one but last exon as end exon.