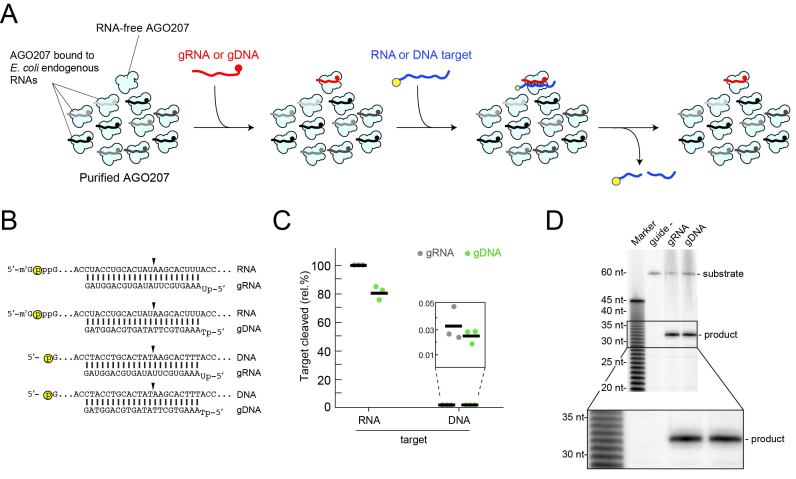
Figure 1.
DNA-guided RNA cleavage activity. (A) Schematic of cleavage assay using ss gRNA or gDNA. RNA-free AGO207 is shown with AGO207 bound to endogenous E. coli RNA that co-purifies with the protein (black and gray strands). Either gRNA or gDNA is loaded into the RNA-free population of AGO207. Following complex formation, a 5′ labeled 60-nt unstructured RNA or DNA target whose sequence perfectly matches the guide is added to the reaction. Yellow circle indicates 32P radiolabel. (B) Schematic of guide and target pairs used in the cleavage assay described in (A) showing combinations of gRNA or gDNA bound to a complementary cap-labeled RNA target or a 5′ end-labeled DNA target. Yellow circle indicates radiolabel. Black arrowhead indicates cleavage site. (C) Cleavage assay using guide and target pairs shown in (B). Black bars indicate average of three independent replicates and dots indicate cleavage percentage of each individual replicate relative to the canonical gRNA targeting the RNA substrate. Inset shows low-level cleavage of DNA targets by either RISC or DISC. (D) Analysis of cleavage site by RISC and DISC. AGO207 was programmed with either a 23-nt gRNA or gDNA followed by addition of a perfectly matched cap-labeled target RNA. Substrates and products were resolved on 16% denaturing PAGE alongside base-hydrolyzed polyuridine RNA. Inset shows expanded view of cleavage products, demonstrating that RISC and DISC both cleave the RNA substrate at the same position.