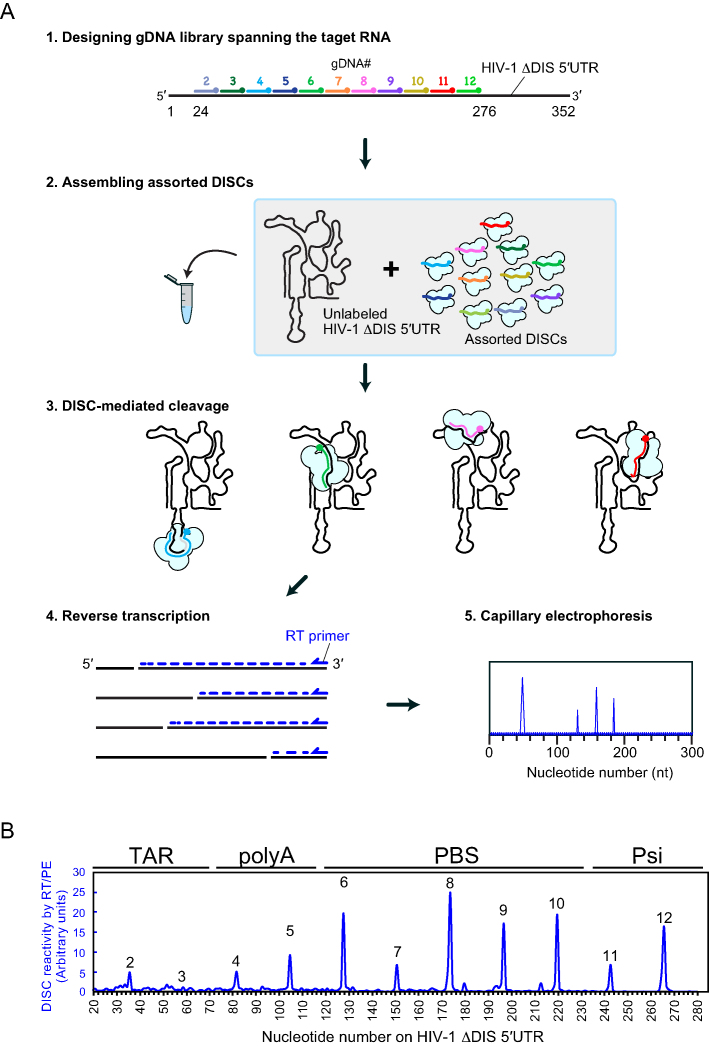
Figure 6.
High-throughput detection of DISC-mediated cleavage events. (A) Schematic of high-throughput assay to detect accessibility of structured RNAs. Guide DNAs spanning the target sequence were mixed together to assemble a mixed population of assorted DISCs. For clarity, AGO207 molecules bound to endogenous E. coli RNA are not shown. An unlabeled HIV-1 ΔDIS 5′UTR was added to the mixture to initiate cleavage. Cleaved RNA products were used as templates to prime reverse transcription using a fluorophore-labeled DNA primer. The cDNA products were detected by capillary electrophoresis yielding an electropherogram of peaks whose positions reflect DISC cleavage sites. (B) Electropherogram of DISC-cleavage sites programmed using 11 gDNAs with 23-nt increments. The average of three individual replicates was plotted as a single trace. Cleavage events were detectable at different sites with varying sensitivity.