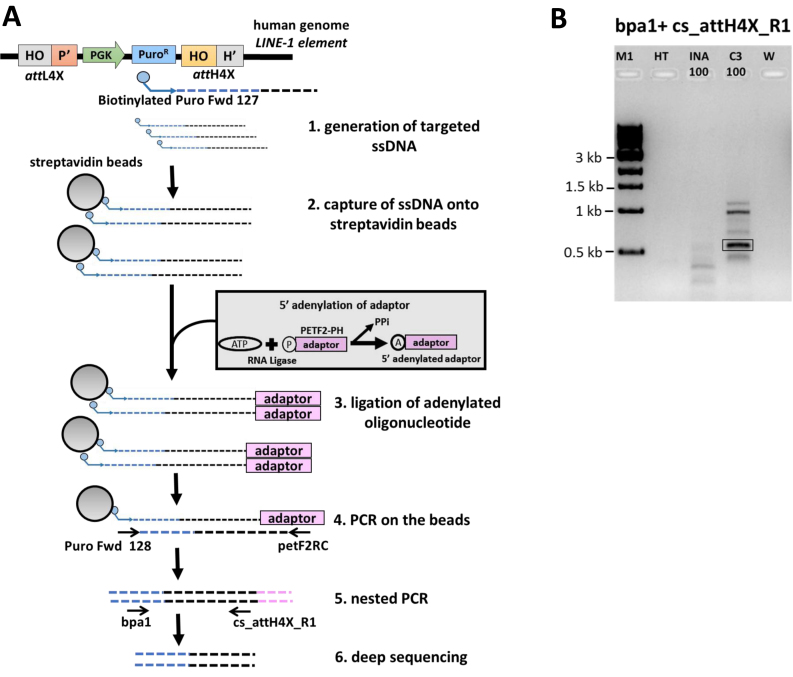
Figure 3.
Seamless vector genomic insertion site mapping via deep sequencing. (A) An illustration depicting the PCR strategy for mapping insertion sites of seamless vector attL4X-PGKssPuro in human HT1080 cells. This includes generation of targeted ssDNA using a biotinylated primer complementary to the inserted vector sequence (step 1), capture of the ssDNA with streptavidin beads, ligation of adenylated oligonucleotide (adaptor) and PCR amplification and sequencing analysis (steps 2–6). Positions of the relevant primers used to map attH4X (right junction) are indicated in step 5. (B) PCR analysis for mapping insertion sites from HT1080 bulk cell culture. PCR with the primers bpa1 and cs_attH4X_R1 (see step 5 in Figure 3A), using bulk genomic DNA from co-transfections of 100ng of attL4X-PGKssPuro and pCMVssInt-C3CNLS resulted in a specific band (highlighted), that was not observed with bulk genomic DNA from control co-transfections of 100 ng of attL4X-PGKssPuro and pCMVssIna. M1, 1 kb ladder; HT, genomic DNA from parental HT1080 cells; INA_100: bulk genomic DNA from co-transfection of 100ng of attL4X-PGKsspuro and 1 μg Inactive Int; C3_100: bulk genomic DNA from co-transfection of 100 ng of attL4X-PGKsspuro and 1 μg Int-C3. W: no DNA template control.