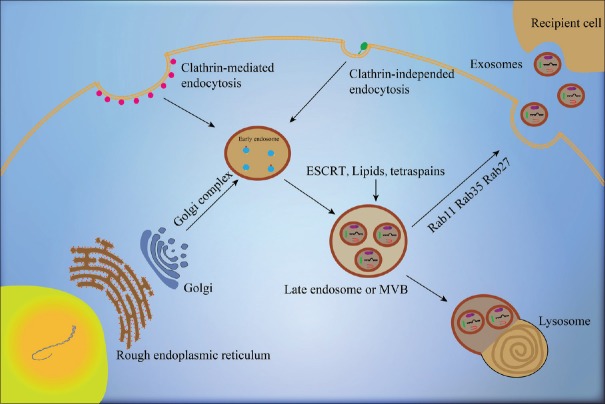
Figure 1.
Mechanism of exosome biogenesis and secretion. EEs are generated through internal budding of the plasma membrane, which may be inward invaginations mediated or not mediated by clathrin. EEs interact with the Golgi complex and form LEs, which then form ILVs, i.e., exosomes, through internal budding of the plasma membrane. ESCRT, lipids, and tetraspanins participate in the formation of ILVs. Some of the MVBs formed are transported by associated RAB proteins (RAB11, RAB35, and RAB27) to fuse with the plasma membrane and are then released into the extracellular space as exosomes. Some other MVBs fuse with lysosome for degradation. The red points represent clathrin and the green points represent lipid raft-associated GPI-anchored proteins. EEs: Early endosomes; LEs: Late endosomes; ILVs: Intraluminal vesicles; ESCRT: Endosomal sorting complex required for transport; MVBs: Multivesicular bodies; GPI: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol.