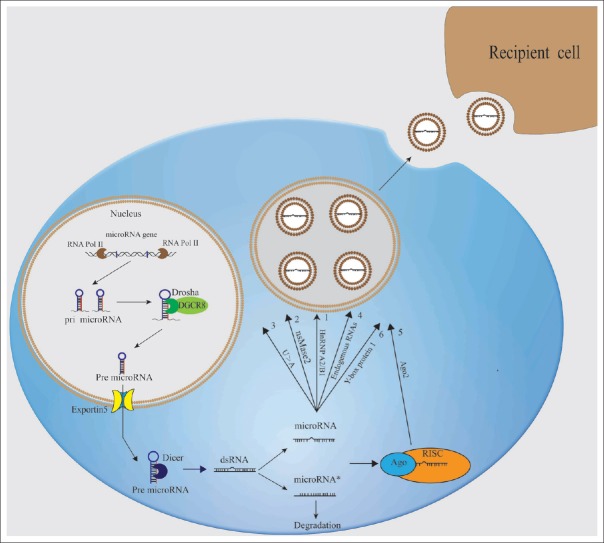
Figure 2.
Mechanism of miRNA formation and sorting mechanism for exosomal miRNAs. miRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II as pri-miRNAs, which are processed using two cleavage events to produce mature miRNA. The primary cleavage of animal pri-miRNA is located in the nucleus and produces miRNA precursors with a length of 70 nt and a stem-loop structure, which are referred to as pre-miRNA. The secondary cleavage is located in cytoplasm where pre-miRNA is cleaved to mature miRNAs with 21–23 nt. The cleavages in the maturation process of miRNA are catalyzed by two types of RNase III, i.e., Drosha and Dicer, respectively. Then, the mature miRNAs incorporate into RISC to form a miRISC complex. Mature miRNAs are sorted into exosomes through six mechanisms: (1) the miRNA motif and hnRNPA2B1-dependent pathway, (2) nSMase2-dependent pathway, (3) 3'-end of the miRNA sequence-dependent pathway, (4) endogenous RNA-mediated pathway, (5) Ago2-dependent pathway, and (6) (YBX1)-dependent pathway. pri-miRNA: Primary miRNA transcript; miRISC: miRNA RISC; hnRNPA2B1: Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1; nSMase2: Neutral sphingomyelinase 2; YBX1: Y-box binding protein 1; miRNAs: microRNAs.