Figure 6.
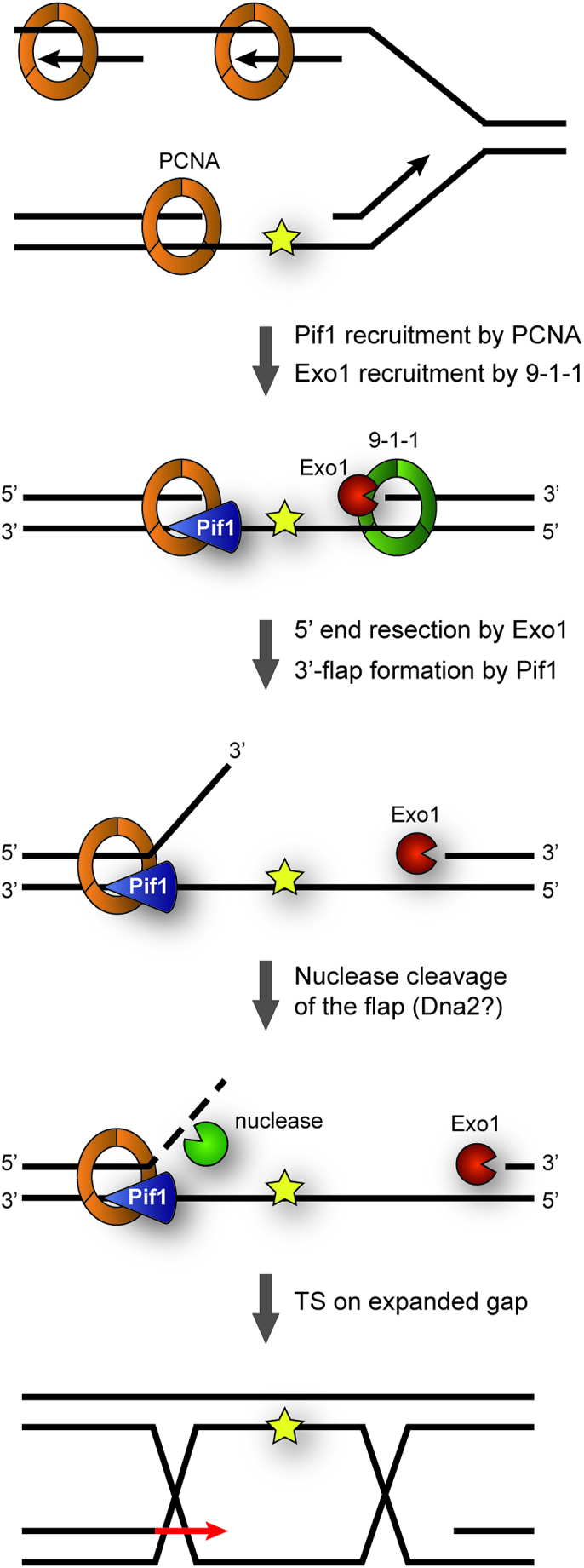
Model for contributions of Pif1 and Exo1 to TS. Replication through damaged DNA generates daughter-strand gaps behind replication forks due to re-priming events. These gaps are expanded at their 5′-junction via Exo1’s 5′-3′-exonucleolytic activity in cooperation with the 9–1-1 checkpoint clamp. Pif1, recruited via interaction with PCNA, contributes to gap expansion at the 3′-junction by generating ssDNA 3′-flaps that subsequently undergo nuclease cleavage, possibly via Dna2. In this manner, gap expansion facilitates invasion of the damaged strand into the newly synthesized sister chromatid, thus initiating TS.
