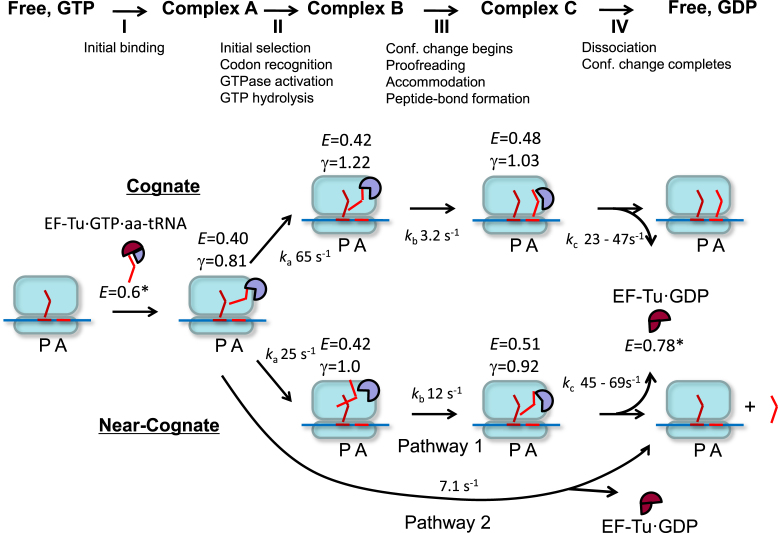
Figure 5.
A kinetic model of interactions between EF-Tu and the ribosome. Actual FRET efficiencies (E), QY ratio correction factors γ, and reaction rate constants ka, kb, kc were determined for dual-labeled EF-TuAV-33/351·GTP·Phe-tRNAPhe interacting with 70SICs programmed with both cognate and near-cognate mRNAs (Table 1). The 70S ribosome is shown in light blue, the mRNA is a blue line, while tRNAs and their corresponding codons are shown in shades of red as bent lines. EF-Tu is shown as a circular sector with different degrees of opening representing different conformations. Classical, GTP-like conformations of EF-Tu are indicated in lavender (FRET states with E in the range from 0.40 to 0.51), while a maroon color is indicative of the classical GDP-like conformation (FRET state E = 0.78*). Thus, the initial FRET state E = 0.6* within the unbound ternary complex, is colored in a combination of maroon and lavender. In the near-cognate case, approximately half of the EF-Tu molecules have no significant FRET or γ change and dissociate with a rate constant of 7.1 s−1 (Pathway 2). kc is given as a range corresponding to ± 1 standard error of the mean. *The FRET values for complexes in solution were determined by (6). These values are not corrected for γ, as the relative QYs and detector sensitivities were not measured in that study. Since the apparent FRET efficiency values for ribosome-bound complexes in (6) (EApp2 values in Figure 3F and G) are similar to the values obtained here, the apparent FRET values for EF-Tu·GTP·aa-tRNA and EF-Tu·GTP in solution are suitable for comparison here.